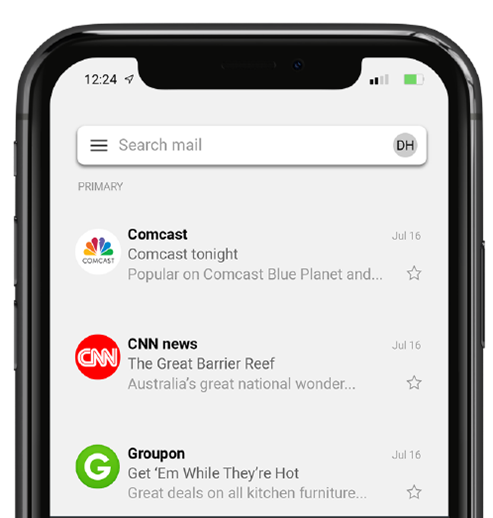
What is BIMI – Understanding BIMI & How It Can Help Prevent Malicious Threats
Monitor the incoming emails and tighten their organization’s email security with BIMI.
BIMI or ‘Brand Indicators for Message Identification’ is an open system used by businesses to check an email’s authenticity, which works on similar lines with DMARC, SPF, and DKIM. The critical feature of BIMI is that while SPF and DKIM take authentication from incoming mail servers, BIMI can check an email’s authenticity while it is in the inbox.
It works on the principle that emails sent from genuine businesses will contain a brand logo. BIMI looks for this symbol to verify the sender’s authenticity. If there are no logos or identifiable attributes, then the email will be listed as spam or originating from an unreliable source. Users can verify an email’s authenticity by merely checking for these logos.
Table of Contents
How Does BIMI Work?
The BIMI works differently at the sender and the receiver sides. At the sender side, the following steps take place.
- Initially, a DMARC authentication will be set up at the domain.
- A BIMI text record will then be published in the DNS (Domain Name System). This text record will contain information on where a mailbox provider can find logos in the email. A URL will be stored in the text record, including a square SVG file of the logo in HTTPS.
- An email is also sent to the subscriber with the header section containing information for mailbox providers to use DMARC and BIMI records to verify the email’s authenticity.
Similarly, at the receiver end, the following steps take place.
- After receiving the email at the mailbox provider, the system looks for a DMARC record for initial authentication.
- After that, BIMI records will be checked in the domain of the DNS.
- Finally, suppose the BIMI text record is correct, and the email passes DMARC authentication. In that case, the provider retrieves the logo from the specified location and displays it near to the subject in the email.
Source: securityboulevard.com
Features Of BIMI
BIMI’s approach is similar to DKIM and has many similarities in its features, as discussed below.
- BIMI requires minimal infrastructure for deployment.
- No attempts are made to add encryption techniques before data transmission.
- There is no dependency on any internet protocol or any other service.
- Transparency is a crucial feature, and BIMI authentications are compatible with existing email infrastructures.
- BIMI also permits delegation of indicator hosting to external platforms.
- Furthermore, BIMI can be deployed incrementally and independently, regardless of clients, to reduce the deployment time.
How BIMI Will Benefit Businesses?
Although BIMI is primarily a technique to allow users to identify genuine emails from a bulk of unverified emails, it also offers other benefits due to its business-oriented characteristics, as described below.
- Building Customer Confidence: With a brand logo, the clients will find the brand more trustworthy. Such a solution also helps prevent sent emails from being marked as spam.
- Improved Email Engagement: Since the emails are identified as safe and not sent to quarantine, they have a higher chance of conversion rates for businesses. Users are more likely to use products from such businesses.
- Based On DMARC: Since BIMI is developed along with DMARC authentication, it forms a multi-layered framework, providing an extra layer of security.
- Visual Confirmation: Since the logo is proof of the email’s authenticity, users will be more willing to open the emails listed as safe and from identifiable sources.
Is DMARC Still Required In Addition To BIMI?
Although BIMI can provide authentication features to an organization, it is still recommended to use DMARC as it helps organizations to maintain their reputation. Moreover, DMARC, with a quarantine or reject policy, is supposed to be deployed with SPF and DKIM for keeping a trustworthy name among domains and avoiding getting blacklisted. Therefore, both BIMI and DMARC are necessary to provide maximum security, as a logo alone will not make the email look one-hundred-percent reliable and free from malware.
Main Security Considerations
BIMI uses brand indicators for domain owners, end-users, and mail receivers. However, it is still prone to malicious actors’ security exploitations. Hence the following safeguards are maintained.
- Metadata In Indicator’s Headers: Any metadata should be removed to avoid bigger file sizes. It can be done using MTA (Message Transfer Agent) or MVA (Mark Verifying Authority) by inspecting and eliminating unnecessary information.
Slow DNS Queries: Most email servers have a built-in predefined timeout for DNS queries to avoid malicious actors’ exploitation attempts. Moreover, caching enables systems to load previously loaded data without establishing a complete connection with the source. - CGI (Common Gateway Interface) Scripts In Indicator Payload: MVAs and MTAs periodically ensure that indicators are of defined size and pass security checks. Besides, MTAs may sometimes cache indicators and serve it to MUAs (Mail User Agents) to bypass malicious payloads.
- Copycat Indicators And Domains: Domain owners are supposed to maintain a reputation with the MTA. Therefore, BIMI will pass emails at the recipient’s end after verifying authentications. The receiver maintains a database of authentic sources which will be cross-checked with the incoming emails to avoid emails from duplicate or forged sources.
- Buffer Overflows: To avoid cyber-attacks using information overload, the MTA or MVA will check for indicators with large file sizes and prevent them.
- Unsigned BIMI: If SPF is used instead of DKIM authentication, then there will be many complications that the domain owner will have to face while adding requirements. Besides, receivers using BIMI may need DKIM while deciding whether to add a BIMI location header on the sender side.
Despite being a powerful open system that distinguishes between trustworthy and unreliable messages, BIMI has various other business-oriented advantages besides technical applications. Most importantly, the approved logo symbol is a sign of authenticity and brand reputation and nurtures customer confidence.
However, BIMI alone is not sufficient to provide maximum security to all clients. It requires DKIM, SPF, and DMARC for tightened cybersecurity and maintaining domain reputation. Finally, BIMI also ensures the deliverability of emails through relevant authentication and forwarding of emails into the user’s inbox. Due to the versatile applications of BIMI, it is expected to expand its features across various platforms in the future as either a separate solution or an integrated subsidiary for its clients.
Join the thousands of organizations that use DuoCircle
Find out how affordable it is for your organization today and be pleasantly surprised.
Interested in our Partner Program for MSPs and VARs? Visit Our MSP Partner Program.