What is DMARC? Domain-based Message Authentication Explained
Learn advantages of deploying DMARC and maintaining DMARC reports.
The DMARC standard was published first in 2012 to prevent email abuse. Many industry leaders like Paypal, Goggle, Yahoo, and Microsoft worked together to design the DMARC specification. Taking inspiration from the SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail), the popular email authentication technologies, they created the online DMARC report framework.
DMARC was initially developed as an email security protocol. Today, an increasing number of email marketers consider it crucial to improve deliverability and online security.
Table of Contents
(DMARC Authentication Process)
Comparing Emails with and without DMARC authentication
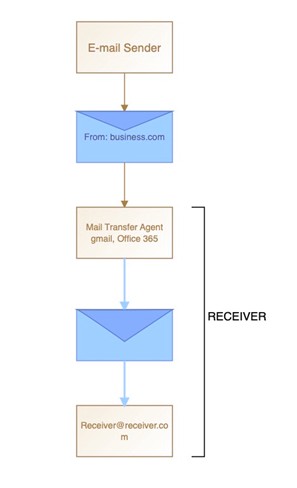
Without DMARC authentication
- The sender sends an email from their domain (business.com) to the receiver’s inbox (receiver.com)
- receiver.com’s Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) has no mechanism to authenticate the email sender (business.com)
- There is no mechanism in the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) of the receiver to authenticate the domain (business.com)
- Hence, receiver.com delivers all the emails from business.com to the recipient’s inbox without validating them.
- In case a hacker impersonates business.com and sends a fraudulent email, the email lands in the receiver’s inbox.
(Email Without DMARC Authentication)
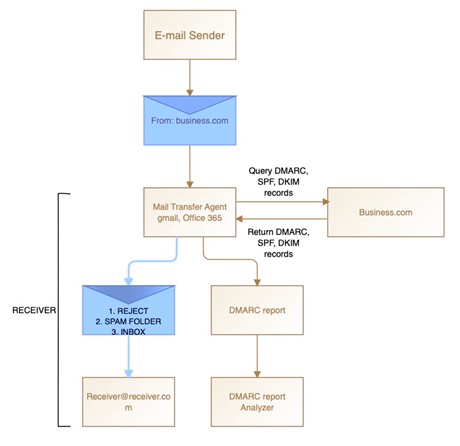
With DMARC Authentication
- The sender sends an email from their domain (business.com) to the receiver’s inbox (receiver.com).
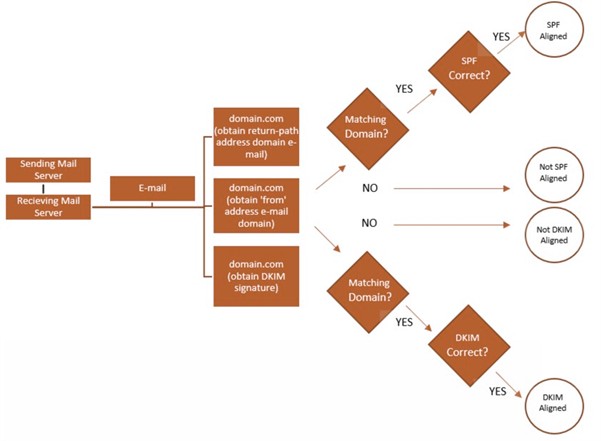
- The Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) of the receiver will look up the DMARC, SPF, and DKIM records of the sender (business.com) for authenticating it.
- If the MTA authenticates the sender, the email proceeds to the recipient’s inbox. Otherwise, it quarantines or rejects the email.
- The MTA generates DMARC reports and sends them to the DMARC report analyzer open source.
(Email With DMARC Authentication)
DMARC Policies
Organizations that use DMARC can define how they want receivers handling mails that fail DMARC checks. They can choose from one of the three policies, which are:
- none: monitor the results without taking any specific action for failed messages. Enterprises use this policy to start gathering DMARC reports and analyze the data in these reports.
- quarantine: Put the messages failing the DMARC checks in quarantine. In simple terms, it means moving such messages to the junk folder.
- reject: Reject all messages failing the DMARC checks.
What Is DMARC: Understanding The Format Of A DMARC Record
The DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance) record forms the core of DMARC implementation in which organizations define the rulesets. It informs the receivers whether a domain has a DMARC setup. If yes, the DMARC record contains the DMARC report format which the organization wants to use. Thus, after implementing the DMARC DNS record, the domain owner can start using DMARC. The email receivers who have adopted DMARC will use the DMARC record to track the enterprise domain’s messages.
Domain owners who choose to publish the DMARC record can define how to handle non-compliance. They can monitor the messages until they are delivered. If they do not get delivered, they can either be rejected or moved to the junk folder.
Adding DMARC Record for Your Domain
Any user who wants to get started with DMARC needs first to publish the SPF and DKIM records. Once they put the DKIM and SPF records in place, they can configure the DMARC when adding policies to their domain’s TXT records. The TXT record name must be similar to “_dmarc.your_domain.com.” And you have to replace “your_domain.com” with your’s or your organization’s domain.
Since the DMARC policies get published as TXT records, they define the further course of action for an email receiver if it receives a non-aligned email.
(Note: If you want to update your DMARC records yourself, you will have to check with your provider who takes care of your domain’s DNS settings)
Maintain Email Deliverability, Along With Server Reputation While Thwarting Malicious Actors
DMARC is the email validation system that protects the organization’s domain from the hackers’ prying eyes, who can use it to launch phishing scams, spoofing attacks, and other cybercrimes. When organizations publish online DMARC records in their DNS, they gain crucial insights into their domain’s senders. Hence, they can gather detailed information regarding their email channel, bringing them in control over who sends emails from their domain on their behalf.
Website owners must make sure that their visitors or clients can only view emails originating from them. Hence, it becomes crucial for every domain owner to use DMARC reports to secure their emails. The receivers derive satisfaction from the fact that they are receiving a legitimate email. At the same time, businesses’ domain addresses are positively impacted in a way that their rate of email deliverability and the server reputation keeps increasing with every delivered email.
Other Benefits of DMARC
- If someone tries to spoof your domain and send malicious emails impersonating you, you can blacklist the abusive IP.
- It will help you boost your brand by entrusting your customers that they are safe when doing business with you.
- It maximizes the delivery of crucial emails by helping you to figure out the reasons for deliverability issues and fixing them at the earliest.
- Since SPF and DKIM function independently, they offer limited protection against email-based threats. DMARC offers maximum security because it leverages both of these technologies to provide more advanced protection.
- The daily aggregate DMARC reports keep you informed about the emails which pass or fail the DMARC check on your domain.
Organizations can address the inherent limitations of email authentication tools like SPF and DKIM by allowing senders and receivers to share information. Senders will inform the receivers how to handle a message which does not authenticate, while receivers will enlighten the senders about their mail authentication infrastructure. DMARC reports work on this collaboration system between receivers and senders to enable the receivers to reject unauthorized messages and improve mail authentication practices for the senders.
Join the thousands of organizations that use DuoCircle
Find out how affordable it is for your organization today and be pleasantly surprised.
Interested in our Partner Program for MSPs and VARs? Visit Our MSP Partner Program.