What Is RUF Or DMARC Forensic Report And How It Can Help Your Business In Email Deliverability Tracking
RUF is a technique used to report to the sender about such failure in delivering the message to the recipient.
DMARC Forensic Report, otherwise known as RUF, is a feature that allows users to view the status of an email that they sent to a particular destination but failed DKIM, SPF, or DMARC authentication. The report passed to the sender will contain detailed diagnostic reports on what went wrong and how the problem could be rectified.
The type of failure will be denoted in the ‘fo’ tag in DMARC records, and the recipient of the failure report will be indicated inside the ‘ruf’ tag. For instance, ruf = mailto:xxxxxxx@ondmarc.com sends the forensic report to the specified email address. By default, such notices are sent only when both DKIM and SPF fail and help identify spoofing attempts with the sender’s IP address availability.
Table of Contents
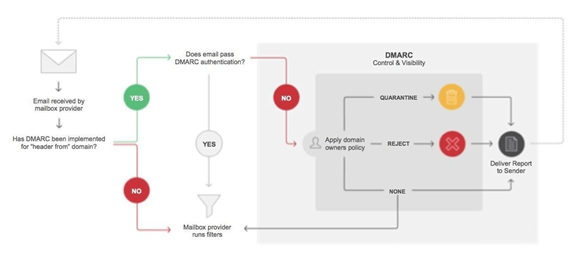
How Does It Work?
RUA or ‘DMARC Aggregate Report’ contains authentication details of DKIM, SPF, and DMARC, whereas the forensic report or RUF includes a header, attachment, URLs, and subject lines. The entire reporting procedure takes place in the following steps.
Image source: Mailjet.com
- The emails are sent with DMARC records, including ‘ruf’ tags with the sender email ID to report authentication failures.
- ISP creates the forensic reports if the DMARC does not align with the SPF or DKIM authentication, or in other words, DMARC authentication fails.
- Forensic reports contain message-level data, IP address, source, mail-stream, and sometimes, the email body.
- DMARC usually does not send the email body unless the client uses the PGP key in the DMARC analyzer.
- If the user uploads a public key, then the DMARC analyzer only sends encrypted messages and neglects messages that are not encoded.
- Users can decrypt the emails using a private key available locally, and the information will be available to users.
What Information Does RUF Contain?
RUF is a complete forensic report and may even contain the entire email that was sent. However, due to the increasing demands of privacy and information security policies, many organizations have been avoiding using RUF forensic reports for preventing data breaches and other cyber threats. The information included in RUF has
- Domain information, such as ‘from’ address, mail ‘from’ address, and DKIM ‘from’ address
- Message identifiers
- IP-related information
- Subject line
- Time of receiving the email
- Authentication results, which include DKIM, SPF, and DMARC results
- ISP (Internet Service Provider) information
- URLs
- Delivery result
The Need For RUF Reports
Besides containing the entire forensic report, RUF also plays some other crucial roles when organizations implement it. The key benefits of using RUF reports are discussed below.
- Instant Notification: If the DMARC authentication fails, the original author receives the forensic reports immediately.
- Identify Unauthorized IPs: Detailed diagnostic reports will contain information on all connected IPs and help organizations pinpoint any unauthorized or suspicious connections.
- Information Per Email: Since RUF reports are available for an individual email, it allows users to find separate detailed information regarding each email.
- Quickest Rectification: Since issues are reported immediately, administrators can discover any malicious elements at the earliest and implement mitigation plans as required.
Setup To Receive RUF Report
To receive the RUF report, first, a DMARC record needs to be created. This DMARC record will enable other DMARC reporting organizations to respond to senders with RUF if any failure occurs. Furthermore, the DMARC record will contain the RUF tag in the specified format, as shown here.
tag: ruf = mailto: xxxx@domain.com
The email ID will be the endpoint for the DMARC to prompt businesses to report back to the sender on any DKIM or DMARC authentication failures.
Why Do Some Generators Not Send Out Forensic Reports?
There might be many reasons why various generators don’t send RUF reports to the sender despite authentication failures, as discussed below.
- Volume: Since a RUF report is created for each email, malicious actors can use it as an opportunity to conduct a DoS attack and slow down a network with redundant requests. It will lead to unaccountable resource utilization when thousands of such forensic reports are generated.
- Privacy Issues: Some generators might be stringent regarding privacy issues. Since the emails contain PII (Personally Identifiable Information), such generators will not send out RUF reports to the senders.
- Not Required: Some organizations can handle authentication failures without DMARC, and some do not even use RUF due to privacy concerns. In simple words, for businesses that do not have DMARC enabled, no RUF reports will be sent to the source.
Limitations Of RUF Reports
DMARC failure or forensic reports contain more information regarding authentication failures in contrast to aggregate reports. However, it has the following limitations too.
- Distracts From Enforcement: Many professionals confuse RUF as proof since it contains detailed diagnostic reports. However, forensic reports cannot be used as a complete enforcement policy.
- Exposes PII: PII or Personally identifiable information may be present in the body of some emails. Suppose any malicious actor gains unauthorized access to the network and views the forensic reports. In that case, they may use the PII for further exploitation.
- High False-positive Rate: The delivery of emails through various forwarders can cause errors in DMARC. As a result, when the data reaches the final destination, DMARC authentication can fail, which causes the generation of RUF reports. Although the error rate is lower, when millions of emails are sent every day, the volume of RUF reports generated will be high and time-consuming to deliver.
- Not Actionable: Although the forensic reports can contain information on unauthorized IPs connected to the network, the administrators have limitations in implementing further legal actions against malicious actors.
RUF reports have various advantages and limited demerits for being a robust email authentication measure. For businesses and individuals who would like to know what went wrong with their sent email, why it remained undelivered, and their sent email shows failed DMARC, they can unquestionably opt for RUF.
Join the thousands of organizations that use DuoCircle
Find out how affordable it is for your organization today and be pleasantly surprised.
Interested in our Partner Program for MSPs and VARs? Visit Our MSP Partner Program.