What Is SPF And The Significance It Holds For Online Businesses
SPF is one such standard that ensures domain reputation and email deliverability.
SPF or Sender Policy Framework is an email authentication technique in which the authorized entities can set a list of approved senders on behalf of the organization. It ensures that no malicious actors can send forged or spam emails from the domain to other organizations, which otherwise could degrade the brand reputation and may put the organization on a blacklist.
SPF was designed to work with SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) since it lacked an exclusive protocol for sending emails between two entities. SPF record is a must-have standard these days in DNS records used in email communication by businesses worldwide for reliable email delivery, thereby maintaining the domain reputation.
Table of Contents
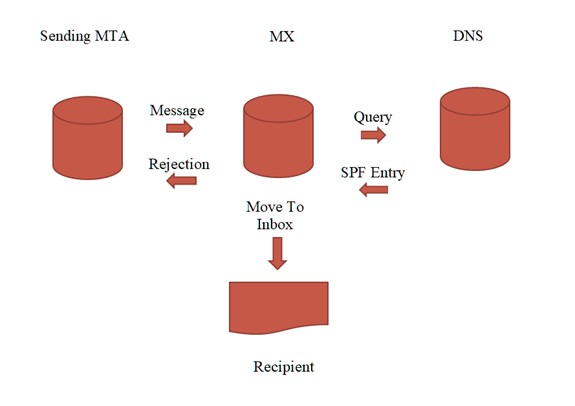
How Does SPF Work?
SPF initially checks the incoming emails and verifies the authenticity of the domain from which the emails originate. The following three steps ensure it.
- The administrator defines the systems and entities that are allowed to send emails from a specific domain. This policy, known as the SPF record, will be stored in every DNS record.
- When the mail server receives an inbound email, the server checks its origin’s IP address, validity, and reputation.
- Further to it, the email server checks the SPF record to understand the domain rules and decide whether to accept, reject, or quarantine the inbound message.
Fig: Working of SPF
When To Use SPF
SPF is used when organizations need to conduct digital transactions or commercial bulk emailing for business purposes. Moreover, SPF is a requirement as per some ISPs (Internet Service Providers). ISPs use secondary email filtering on invalid SPF records, and the emails are blocked or quarantined if SPF authentication fails.
The Two Major Objectives of SPF
Organizations use SPF to meet the following fundamental requirements:
- SPF identifies spam messages, allowing early detection of spam and spammers while blacklisting suspicious and malicious sources.
- The SPF’s precautions also enable organizations to keep up their reputation and not get degraded by malicious actors’ interference.
Misconceptions On SPF
While SPF offers many benefits, it also has its limitations and is not completely secure against all cyber attack strategies. Thus, it is necessary to use the framework depending on the environment and execute it in conjunction with other frameworks for maximizing security. Here are some notions about SPF and their clarification.
- SPF is utterly secure against spoofing: SPF record cannot protect the sender’s visible address since it works with the ‘from’ address or the return path in emails.
- Complete protection against spamming: Even though SPF blocks emails from malicious sources and rejects suspicious emails to a certain extent, it does not identify all incoming spams.
- There can be more than one SPF record per domain: A user can only have one SPF record for sending an email. For a domain having more than one record, the recipient domain declines all the entries, and the emails fail the SPF check.
How To Overcome The Drawback?
SPF is not the complete authentication standard, and it has its drawbacks. A significant disadvantage is that malicious actors can circumvent the IP address checking process. However, SPF can still be useful when used with DKIM and DMARC. DMARC is a more robust protection measure against spoofing. Moreover, it provides feedback on the rejected emails to think of what to do with them, which is not SPF’s purpose.
Creating An SPF Record
An SPF record is created based on the inclusions required by IP addresses and third-party domains, and what action has to be applied to the emails it encounters. The following are the steps in brief involved in the creation of an SPF record.
- Mention the SPF version. E.g., ‘v=spf1,’ i.e., the SPF record must start with the SPF version’s mention.
- Now, incorporate the information regarding the systems, such as IP addresses, that can send emails on behalf of the domain.
- Include tags that represent the third-party domains that can send emails on behalf of the organization.
- End the record with the ‘all’ tag. This tag specifies the policy that must be applied to the emails.
Explanation Of SPF Record Syntax
If the above-mentioned steps seem complicated, here is an SPF record syntax example which would make it easier for you to understand:
v=spf1 a mx include:spf.mtasv.net include:_spf.createsend.com ~all
The above is a typical SPF record. The critical elements in the syntax are identified as follows.
v=spf1indicates the version of the SPF used.aindicates that the domain includes the address record ‘A,’ which should match the IP address of record ‘A’ to pass it at the receiver’s side.mxindicates that the recipient server passes the messages as long as it arrives from a domain’s given IP address.include: instructs the receiving servers to add the value of SPF records at specified domains. Generally, these values will be IP addresses added as per some predefined coding.~allindicates that all other communication must be a ‘soft’ fail. It means that at the receiver end, such emails will be accepted but flagged as soft fail. It helps in a more straightforward spam check.
Important: The Significance Of The ‘all’ Tag
As mentioned above, the ‘all’ tag at the end of the SPF record will decide an email’s fate. It can be used in three different forms based on the policy to be applied.
- -all: This corresponds to the ‘Fail’ policy, which means all emails from servers not listed in the SPF record must be rejected.
- ~all: This is the ‘Softfail’ policy that accepts the non-listed servers’ emails, but marks or flags them.
- +all: This option is seldom used, as it means to blindly allow all emails even when they are from the servers not listed.
SPF allows administrators to decide which systems should be permitted to send emails on behalf of the business. It also enables them to limit insider threats to an extent; however, it’s only the first step towards ensuring that. One also has to ensure that their domain also has DKIM and DMARC records. In a nutshell, SPF defines the IP addresses authorized on each domain to send the emails to a target organization or an individual and clearly defined SPF records ensure robust email deliverability.
Join the thousands of organizations that use DuoCircle
Find out how affordable it is for your organization today and be pleasantly surprised.