Forensic DMARC & Aggregate DMARC Reports Explained In Brief
Understand how DMARC aggregate report provides summarized information every day.
Knowing how one’s domain is being used to send emails can be a valuable feature for analysis purposes. Are the emails leaving the outgoing server being delivered to the inboxes? Who is sending the email on behalf of your domain? Are all the emails being authenticated? A dive into the DMARC report can save a user the trouble of having to make guesses. The DMARC aggregate report can even help one make critical decisions. Below, we discuss the concept in brief.
Table of Contents
What Is A DMARC Report?
A DMARC report provides valuable information on the emails that pass or fail authentication. A DMARC record published in the DNS is necessary to receive DMARC reports using the appropriate tags. The DMARC report is typically delivered daily (every 24 hours) unless specified differently using the ri tag in the record. There are two types of DMARC reports:
The DMARC aggregate reports
It contains summarized information on all emails that go through the authentication process. The report provides information such as the sending IP address, email count, SPF/DKIM identifiers and results, etc. The DMARC record points the rua tag to the email specified by the domain owner to receive aggregate reports. For example, rua=mailto:reports@yourdomain.com. The DMARC aggregate report contains various types of information in an XML (Extensible Markup Language) file.
DMARC failure or forensic reports
This report contains individual information regarding email messages that fail DMARC, SPF, or DKIM validation. The DMARC record uses the ruf tag to receive forensic reports. For example, ruf=mailto:reports@yourdomain.com.
How To Read A DMARC Report?
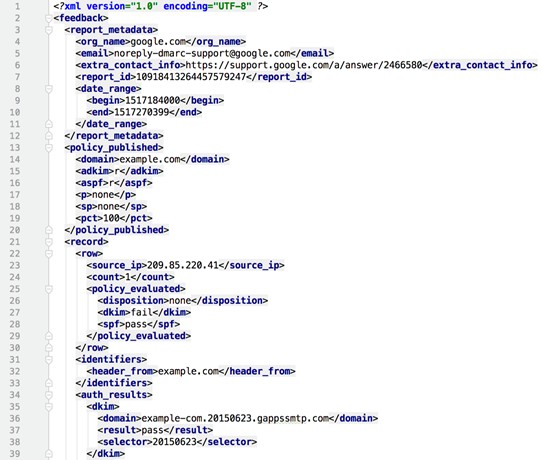
A DMARC aggregate report can be difficult to comprehend at the beginning. The following is a report example from the DMARCLY mailbox.
(Source – DMARCLY)
The reports received daily will contain information such as:
- The domain of the organization that sent the report
- The domain to which the report belongs
- Date range – beginning and ending
- Source IP address
- Email count
- SPF-related information
- Domain
- Outcome: Pass or Fail
- Authentication result: none, neutral, pass, fail, permerror, temperror
- DKIM-related information
- Domain
- Outcome: pass or fail
- DKIM Authentication result: none, neutral, pass, fail, policy, permerror, temperror
- Disposition of the message: none, quarantine, or reject
One crucial point to remember is that the number of records in the report could vary depending on the number of emails sent from the organization.
Using A DMARC Report Analyzer
Since the DMARC report can be lengthy and contains varied information, putting it in an easily understandable form may not be possible manually and on a day-to-day basis. Here is where a DMARC Report Analyzer comes into the picture. A DMARC report analyzer aims to process all the reports and convert them into a readable form using data charts, graphs, etc. Presenting data in user-friendly overviews can greatly help system administrators analyze data quickly, systematically, and timely.
A comprehensive DMARC Report Analyzer must provide a host of features such as:
- Aggregate RUA & Forensic RUF DMARC reports
- Instant notifications
- Unlimited users, domains, and domain groups
- Automated reports
- Tips and suggestions
- An overview of diverse information using charts and templates
- Two-factor authentication
- Automated subdomain discovery
- Domain grouping
- Knowledge center and support services
In a nutshell, the DMARC aggregate report can help remove unauthorized hosts to avoid sending emails on behalf of your organization’s domain and help ensure that the emails are sent or received from authentic sources only.
Join the thousands of organizations that use DuoCircle
Find out how affordable it is for your organization today and be pleasantly surprised.
Interested in our Partner Program for MSPs and VARs? Visit Our MSP Partner Program.