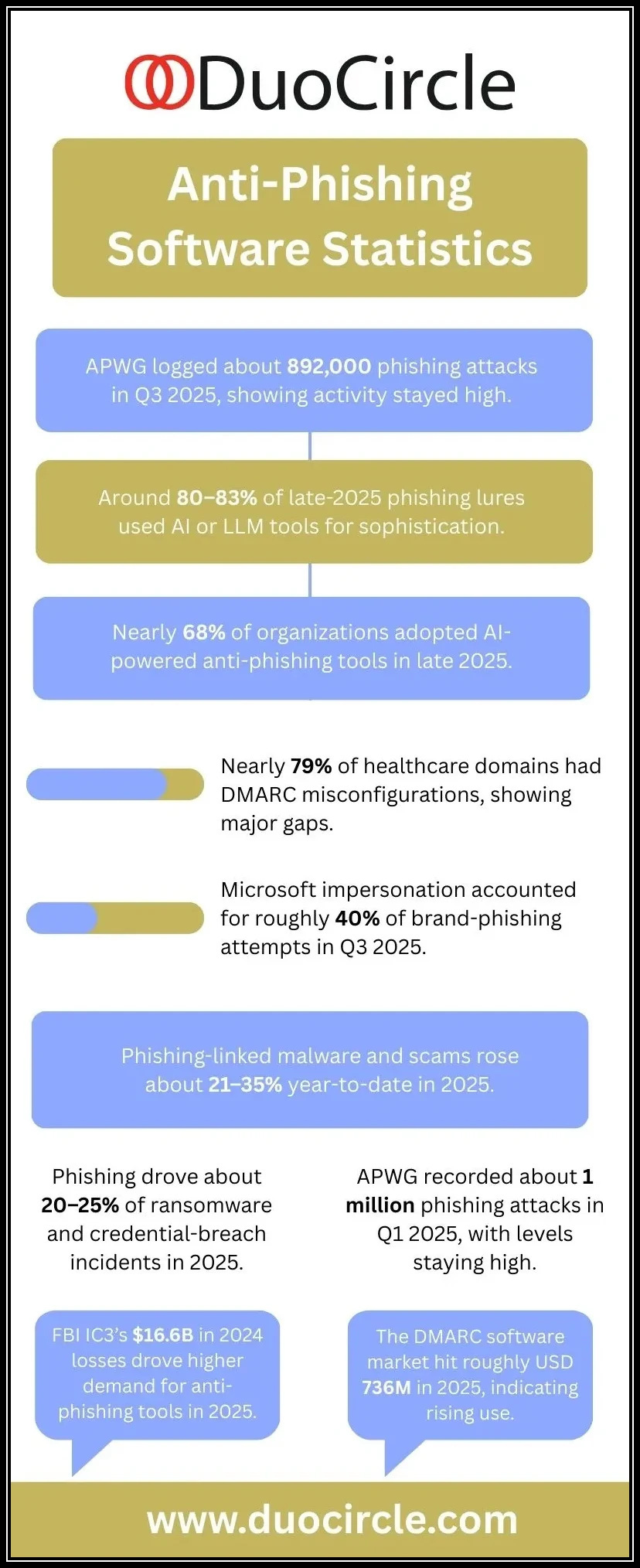
Phishing remains one of the most pervasive and damaging cyber threats targeting individuals and organizations worldwide. At its core, phishing involves cybercriminals using deceptive emails, messages, or websites designed to trick users into divulging sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, or personal identification.
These attacks often leverage social engineering defense mechanisms but exploit human psychology to bypass traditional security controls. Attackers employ spoofing prevention techniques to impersonate trusted entities, increasing the likelihood of successful intrusion.
Common phishing tactics include embedding malicious URLs that lead to credential harvesting prevention sites, using email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to bypass filters, and leveraging phishing URL blocking to stop delivery of harmful links. More advanced techniques involve zero-day exploit protection to exploit novel vulnerabilities in software, as well as exploiting domain-based message authentication weaknesses to masquerade as legitimate senders.
Modern phishing campaigns focus not just on mass spam but on targeted spear-phishing, which uses cyber threat analysis and threat intelligence to tailor attacks to specific individuals or organizations. This elevates the risk of identity theft prevention and financial fraud, posing a severe threat to corporate email protection strategies.
The Evolution of Phishing Techniques
Phishing methods have significantly evolved from simple spam emails to sophisticated, multi-layered attack campaigns. Early phishing primarily relied on basic spam filtering techniques, which many legacy cybersecurity software solutions attempted to block with limited efficacy. However, cybercriminals advanced their approaches by incorporating malware protection evasion, leveraging malware payloads alongside phishing emails in hybrid attacks.
The transition to cloud security environments introduced new attack surfaces, requiring more robust anti-fraud tools and intrusion prevention. Attackers now use dynamic URL filtering to redirect users through several malicious layers, complicating detection efforts. Browser security enhancements, including browser extensions for security and SSL inspection, are deployed to counter phishing attempts that utilize compromised websites.
Moreover, phishing simulation combined with security awareness training helps organizations assess human vulnerabilities and enhance cyber hygiene. Companies like KnowBe4 specialize in such training, helping employees recognize phishing attempts proactively.
Supply chain compromises, social media reconnaissance, and advanced threat protection modules integrated into comprehensive cybersecurity software equip defenders with the ability to counteract newly emerging phishing stratagems. Vendors such as Proofpoint, Symantec, Barracuda Networks, and Trend Micro exemplify these evolving protection solutions.
Why Traditional Email Filters Are Not Enough
Traditional email filters, while foundational for email security, are insufficient against modern phishing attacks due to their limited scope and reliance on static rule sets. Older spam detection algorithms primarily identified phishing attempts using signature-based methods, which fail to detect zero-day exploits or polymorphic phishing campaigns.
Without advanced threat protection features like behavioral analytics and real-time threat monitoring, traditional filters cannot dynamically adapt to emerging phishing tactics. For instance, domain-based message authentication and email authentication protocols may not capture subtle spoofing or homograph attacks used by sophisticated adversaries.
Moreover, traditional filters often lack integration with risk management software and security information and event management (SIEM) systems to provide a holistic defense posture. This deficiency translates into vulnerability to credential harvesting prevention bypasses and delayed phishing incident response.
Consequently, organizations increasingly adopt secure email gateway solutions such as Cisco Email Security, Mimecast, and Microsoft Defender for Office 365, which incorporate multi-factor authentication enforcement, phishing URL blocking, and advanced cyber attack mitigation strategies.
Key Features of Advanced Anti-Phishing Software
Advanced anti-phishing software provides a comprehensive suite of capabilities designed to counter the increasingly complex threat landscape:
- Phishing Detection and Behavioral Analytics: Utilizing machine learning security algorithms to identify anomalous email patterns and user behaviors indicative of phishing attempts.
- Secure Email Gateway Integration: Deploying robust spam filtering, email encryption, and SSL inspection features to ensure safe and authenticated communication channels.
- Endpoint Protection and Network Security: Enforcing malware protection and intrusion prevention measures to block phishing payloads and lateral movement within networks.
- URL Filtering and Phishing URL Blocking: Real-time analysis and blacklisting of malicious URLs to prevent users from accessing known phishing sites; solutions by Google Safe Browsing and web filtering software contribute to this.
- Spoofing Prevention and Email Authentication Protocols: Incorporating SPF, DKIM, and domain-based message authentication to prevent identity spoofing and enhance email trustworthiness.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Support: Reinforcing login security through two-factor authentication and MFA, a critical component in mitigating credential theft.
- Threat Intelligence and Cyber Threat Analysis: Utilizing data feeds from providers such as FireEye, PhishLabs, and Cofense to stay ahead of phishing trends and threats.
- Phishing Simulation and Security Awareness Training: Engaging employees in simulated phishing exercises and educational programs to strengthen human defenses.
- Phishing Incident Response and Cyber Attack Mitigation: Automated alerting, forensics, and remediation capabilities enable rapid containment and recovery.
Brands like Bitdefender, Kaspersky Lab, McAfee, Sophos, and Avast deliver integrated solutions embedding many of these features within their cybersecurity software portfolios to safeguard corporate environments.
How Machine Learning Enhances Phishing Detection
Machine learning security fundamentally transforms phishing detection by enabling intelligent, adaptive, and predictive capabilities. Unlike static rule-based systems, machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets comprising email metadata, user behavior, historical phishing blacklists, and embedded URL characteristics to identify subtle indicators of compromise.
Behavioral analytics models learn normal user communication patterns and flag deviations that may signal social engineering defense failures. For example, if an employee suddenly receives an uncharacteristic email requesting wire transfer authorization, the system identifies it as high risk.
Machine learning also supports spam detection algorithms that evolve to detect novel phishing vectors, including targeted spear-phishing and business email compromise. By integrating with security information and event management systems, machine learning contributes to real-time threat monitoring and automated phishing incident response protocols.
Innovative platforms developed by companies such as Trend Micro Phish Insight, NortonLifeLock, and F-Secure incorporate machine learning in their email security offerings, ensuring continuous improvement and zero-day exploit protection. Similarly, Microsoft Defender for Office 365 leverages AI-driven analytics to enhance its secure email gateway capabilities, reducing false positives and improving threat detection precision.
Combining machine learning insights with traditional cybersecurity frameworks—such as password managers, cyber hygiene practices, email encryption, and network security policies—results in a multi-layered defense that significantly reduces the risk and impact of phishing attacks.
Incorporating advanced anti-phishing software alongside comprehensive security awareness training enhances an organization’s resilience, safeguarding sensitive data and preserving trust in digital communications.
As organizations adopt these cutting-edge defenses, they bolster their overall cybersecurity posture, integrating endpoint protection, cloud security, and cyber attack mitigation into a coherent strategy to protect critical assets from evolving phishing threats.
Integrating Anti-Phishing Tools with Existing Security Systems
Effective phishing detection and cyber attack mitigation require seamless integration of anti-phishing software with an organization’s broader cybersecurity ecosystem. Leading cybersecurity software providers such as Proofpoint, Symantec, and Cisco Email Security emphasize the importance of embedding anti-fraud tools within secure email gateway architectures to enhance email security. By coupling phishing URL blocking with domain-based message authentication, organizations can enforce email authentication protocols that validate sender legitimacy and prevent spoofing.
Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems enables real-time threat monitoring and cyber threat analysis, offering a holistic view of security incidents across endpoints and networks. Behavioral analytics and machine learning security technologies empower these platforms to detect zero-day exploit protection signals and phishing attempts stemming from social engineering attacks. Moreover, endpoint protection software from vendors like Bitdefender and Kaspersky Lab can receive alerts and updates from phishing incident response frameworks, improving intrusion prevention and malware protection across devices.
Additional integration layers, such as URL filtering and web filtering software, work in tandem with browser security plugins and phishing blacklists—services provided by Google Safe Browsing and Avast browser extensions for security—to restrict access to dangerous sites. For comprehensive identity theft prevention, coordinating phishing simulation exercises and security awareness training, as offered by KnowBe4 and Cofense, with risk management software creates a proactive defense posture. This multi-layered approach ensures that corporate email protection complements cyber hygiene efforts effectively.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Anti-Phishing Software in Action
Numerous organizations across industries have demonstrated significant improvements in phishing incident reduction through the deployment of advanced threat protection and anti-phishing solutions. For example, a multinational financial institution utilized Mimecast’s cloud security platform integrating spam filtering, email encryption, and phishing URL blocking to mitigate targeted phishing campaigns, reducing successful phishing clicks by over 70% within six months.
Another notable instance involved a healthcare provider deploying Microsoft Defender for Office 365 alongside Trend Micro Phish Insight for phishing simulation. This combined approach enhanced social engineering defense mechanisms and improved staff recognition of suspicious emails following ongoing security awareness training. The healthcare network experienced measurable reductions in data loss prevention incidents, thanks to the integration of email authentication protocols and secure email gateways.
Barracuda Networks has also helped an educational institution implement web filtering software with SSL inspection capabilities, deploying multi-factor authentication (MFA) and behavioral analytics. This setup fortified their network security and credential harvesting prevention, particularly in combating sophisticated phishing campaigns leveraging zero-day exploit tactics.
Meanwhile, enterprise users of FireEye’s advanced threat protection solutions noted that the coordination between cyber threat intelligence feeds and anti-fraud tools enabled rapid phishing incident response and minimized downtime during attempted breaches. These success stories illustrate the critical role of layered defenses combining malware protection, risk management software, and phishing blacklists in safeguarding organizations against phishing threats.
Choosing the Right Anti-Phishing Software for Your Needs
Selecting effective anti-phishing software demands alignment with an organization’s specific cybersecurity requirements. Key evaluation criteria include the platform’s capabilities for phishing detection accuracy, advanced threat protection features, and compatibility with existing infrastructure such as secure email gateway and SIEM systems. Vendors like Sophos and McAfee offer comprehensive suites that integrate spam detection algorithms, email encryption, and network security modules, while allowing for granular URL filtering and phishing URL blocking.
Organizations prioritizing behavioral analytics and machine learning security will find solutions like Symantec and Trend Micro valuable due to their continuous cyber threat analysis and real-time threat monitoring. For enterprises focused on robust social engineering defense, the integration of phishing simulation tools from Cofense or KnowBe4 with their anti-phishing platform enhances security awareness training efficacy.
Additional considerations include support for multi-factor authentication protocols and credential harvesting prevention mechanisms. Cloud security compatibility and endpoint protection breadth are essential for organizations shifting workloads to hybrid or fully cloud environments. Price points vary widely, so investing in risk management software functionality and ongoing phishing incident response support should drive purchasing decisions.
Best Practices for Users to Complement Software Protection
Even the most sophisticated cybersecurity software cannot fully replace informed, vigilant user behavior. Promoting strong cyber hygiene is vital: users should routinely update passwords via a family password manager to ensure all members remain protected, be cautious with email attachments, and verify suspicious URLs using domain-based message authentication feedback.
Security awareness training programs, incorporating phishing simulation exercises, are instrumental in helping users recognize social engineering tactics and avoid credential harvesting pitfalls. Applying two-factor authentication or multi-factor authentication across corporate systems adds a critical layer of defense that complements malware protection and intrusion prevention technologies.
Utilizing browser security extensions from reputable providers and adhering to guidelines on SSL inspection ensure safe web browsing and minimize exposure to phishing threats. Regular audits of spam filtering effectiveness and reviewing phishing blacklists enhance email security posture. Users must report suspected phishing attempts promptly, aiding incident response teams in mitigating risk effectively.
The Future of Anti-Phishing Technology and Trends
Anti-phishing technology continues to evolve rapidly, with a growing emphasis on artificial intelligence, behavioral analytics, and machine learning security to detect increasingly sophisticated threats in real-time. Cyber threat analysis is becoming more predictive, leveraging global phishing blacklists and threat intelligence integration with SIEM and cloud security platforms for proactive mitigation.
Future advancements may include deeper synergy between phishing simulation and automated phishing URL blocking, enhancing social engineering defense dynamically. Enhanced phishing incident response workflows powered by automation and orchestration are expected to reduce human response times and improve cyber attack mitigation.
Browser security innovations, such as smarter web filtering software with contextual analysis, will further restrict access to high-risk sites. Meanwhile, the integration of risk management software with cybersecurity suites will offer organizations a cohesive approach, managing vulnerabilities alongside phishing detection efforts. Embracing multi-factor authentication and expanding email encryption techniques will remain foundational strategies to combat identity theft prevention and credential harvesting in the years to come.
FAQs
What is phishing detection and how does it work?
Phishing detection involves identifying fraudulent emails and websites that impersonate legitimate entities to steal sensitive information. It uses techniques like spam filtering, URL filtering, behavioral analytics, and machine learning security to flag and block suspicious content before it reaches users.
How do secure email gateways enhance email security?
Secure email gateways provide email authentication protocols, domain-based message authentication, and phishing URL blocking to filter out malicious emails. They protect corporate email by preventing malware, phishing links, and spoofed messages from entering an organization’s network.
Why is integrating anti-phishing tools with SIEM important?
Integration with SIEM enables real-time threat monitoring and centralized logging of phishing-related events. This synergy allows for comprehensive cyber threat analysis and faster phishing incident response, improving overall intrusion prevention capabilities.
How can security awareness training reduce phishing risk?
Training educates users about social engineering defense and cyber hygiene, increasing their ability to recognize phishing attempts and avoid credential harvesting. Regular phishing simulation exercises help reinforce these behaviors by providing practical experience.
What role does multi-factor authentication play in phishing protection?
Multi-factor authentication adds extra verification layers beyond passwords, making it harder for attackers to access accounts even if credentials are compromised. It significantly enhances identity theft prevention and reduces the impact of phishing attacks.
Key Takeaways
- Integrating anti-phishing tools with existing cybersecurity software, such as secure email gateways and SIEM, strengthens overall phishing detection and cyber attack mitigation.
- Case studies from industry leaders like Mimecast, Microsoft Defender for Office 365, and Barracuda Networks demonstrate the effectiveness of layered defenses including behavioral analytics, phishing URL blocking, and security awareness training.
- Selecting the right anti-phishing solution depends on compatibility with organizational infrastructure, support for advanced threat protection features, and integration with phishing simulation platforms.
- Complementary best practices, including regular use of password managers, multi-factor authentication, browser security extensions, and user training, are essential for robust protection.
- Emerging trends focus on AI-driven cyber threat analysis, enhanced phishing incident response automation, and evolving web filtering software, ensuring continued advancements in phishing protection technology.