How do third-party marketing agencies send emails on behalf of clients while staying
It is a common practice for businesses to delegate marketing tasks to third-party agencies. Working with these marketing agencies brings in added benefits such as specialisation in particular niches and cost-effectiveness. These agencies need to take extra care to ensure their emails don’t end up in the spam folder or get rejected.
In order to prevent phishing or spoofing attacks, domain owners often deploy DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance). One of the most popular and effective email authentication protocols, DMARC also discourages domain owners from unnecessarily spamming their subscribers. Emails that fail the authentication check (SPF and DKIM) are moved to the spam folder or rejected right away by DMARC.
So, if you’re a marketing agency working with DMARC-compliant domains, ensure you are one of the authorized senders. This will help you achieve greater visibility, improved email deliverability, engagement, and boosted conversion rates.
Here’s what else you should consider:
- The origin of the email links must be from the client’s domain. But make sure that these email links can be used by your infrastructure.
- The origin of images, as well as other email elements, should also happen from the client’s domain. You must be able to use the same in your infrastructure.
- Tweaking the email delivery server names is also necessary to match them with the client’s domain.
How to send emails from a client’s domain?
This is how you should send emails from your client’s domain to ensure seamless email deliverability and higher conversions:
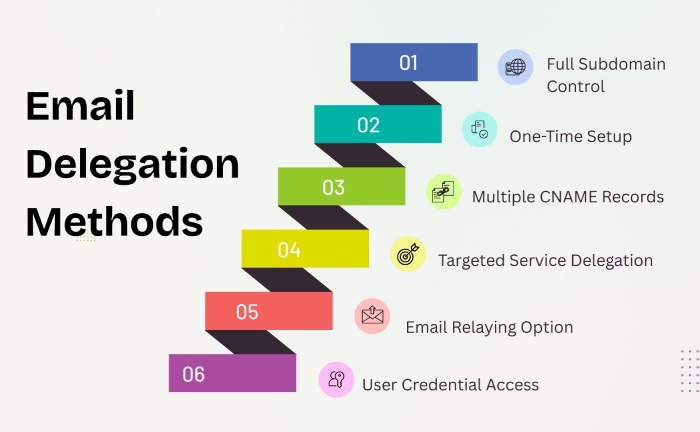
Domain delegation
To be able to send emails on your client’s behalf officially, you must ask them to delegate a subdomain to you. Once delegated, it is your responsibility to manage the subdomain completely. The client can delegate a subdomain to you using either CNAMEs or full delegation.
Now, let’s understand what full delegation and CNAMEs are!
Full delegation
The full delegation method enables the client to delegate a complete subdomain to you. In that case, you will have to bear the responsibility of maintaining it. It’s a one-time process that requires the client to delegate a subdomain to you. Once done, they are free from all obligations. The majority of the clients and marketing agencies prefer using the full delegation approach.
CNAMEs
This involves the creation of multiple CNAMEs by the client. Each CNAME points back to its own domain. The job of each CNAME is to delegate specific services. Generally, clients don’t prefer this approach as it involves the creation of multiple DNS entries in the beginning.
NOTE: CNAMEs are commonly created to configure SPF, support DKIM authentication, address email rejections, and associate email capabilities with the client’s domain.
Relaying
This technique works well when you are required to send only a couple of emails on behalf of your client. The relaying process involves the configuration of emails to be relayed. The configuration has to be done by your client using a different email server. This can be done using two methods: User credential configurations and SMTP relay.
User credential configurations
This technique allows your clients to create user credentials and helps you with an account that is used for sending emails on their behalf. The client will configure your services and enable you to use the new user credentials to send emails.
SMTP relay
An SMTP server acts like an intermediary between the sender’s domain and the recipient’s email servers by forwarding emails from the former to the latter. The SMTP relay enables you to send emails across different domains and networks. Relaying help in routing emails from one server to another in case direct delivery is impossible.
Manual configuration
If you are looking for something simple, the manual configuration approach is the best option. In order to manually configure SPF, the client must add your netblocks to their SPF record. To manually configure DKIM, the client has to add the DKIM-related keys to their DKIM record.
NOTE: The bounce address of the emails should include the client’s domain.
The manual configuration approach requires the client to take care of the one-time configuration process to sign the DKIM keys and add SPF records. As an agency, you will have to take care of the email server functions, which include adding the client’s domain to DKIM signatures and bounce addresses.
Further, you’ll have to update SPF records on a regular basis and make sure the client updates theirs as well.
No matter which method you opt for sending emails on behalf of DMARC-protected domains, your priority as a marketing or a digital marketing agency should be to simplify the process for your clients as well as align the emails with DMARC requirements. For further help, you can connect with email security experts who will take care of the authentication part while you focus on your marketing strategies.