Email hosting servers constitute the backbone of modern business communication infrastructure. At their core, these servers manage the sending, receiving, and storage of electronic mail by leveraging robust email server software. Their configuration involves the integration of various email protocols such as SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol), and POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3), ensuring smooth mail routing between mail transfer agents (MTAs) and mail delivery agents (MDAs). Businesses depend on these servers to provide reliable communication channels facilitated through inbound mail servers, outbound mail servers, and mailboxes with efficient mailbox storage management.
The domain name system (DNS) plays a crucial role, with MX records specifically directing email traffic to the appropriate servers for a domain. Email hosting is offered in various forms, ranging from shared email hosting to dedicated email servers and cloud email hosting solutions. Each type is tailored for distinct organizational needs, balancing cost, performance, and scalability.
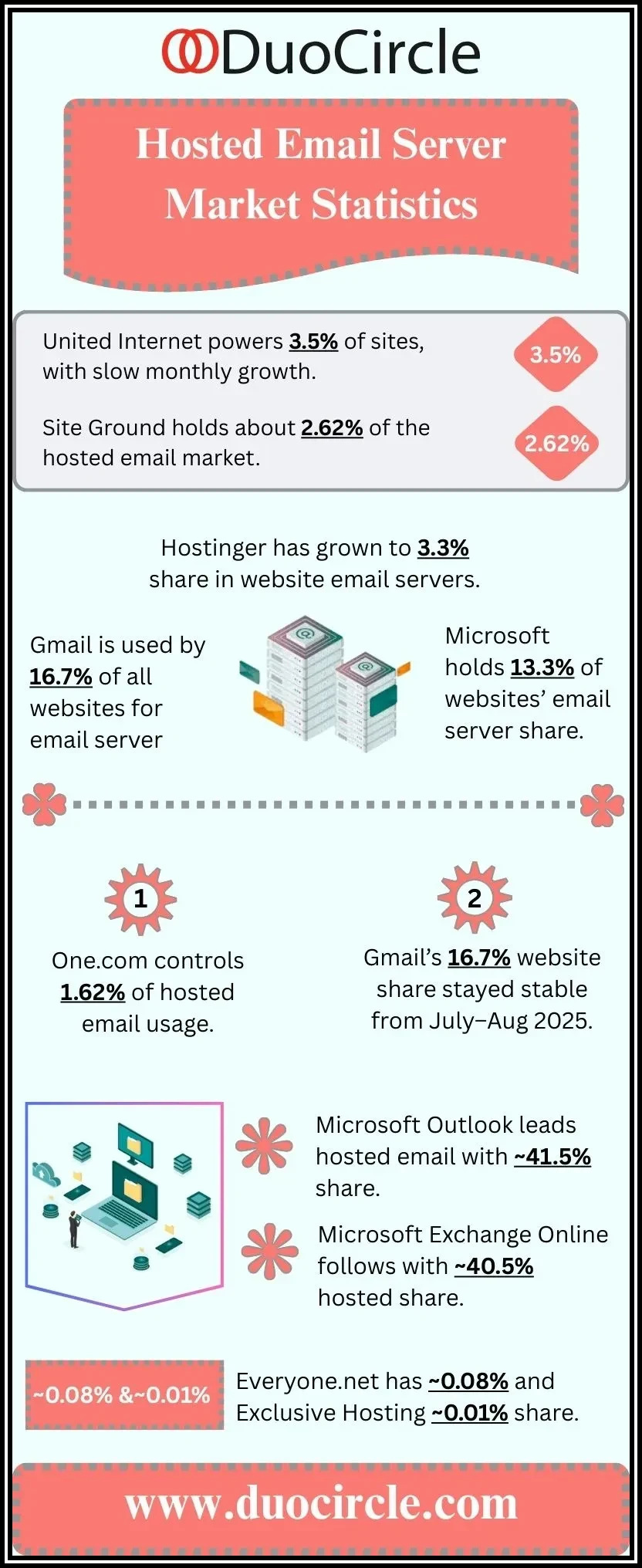
Leading providers like Google Workspace, Microsoft Exchange Server, and Zoho Mail offer comprehensive email server solutions that integrate seamlessly with popular email clients such as Microsoft Outlook and Mozilla Thunderbird, as well as webmail interfaces. Complementary software options include Postfix and Exim for MTAs, while enterprise-focused platforms like SolarWinds Mail Assure and SmarterMail provide advanced features for larger businesses.
Importance of Efficient Business Communication
In the corporate world, communication efficiency directly impacts productivity, collaboration, and client satisfaction. Email remains a fundamental communication medium for internal correspondence, external client interactions, and formal documentation. Efficient email hosting servers ensure minimal downtime and high email deliverability rates, essential for maintaining uninterrupted workflows.
Efficient business communication depends on aspects such as server uptime, fast mail server performance, and effective management of email bandwidth. Furthermore, features like email archiving and email migration support preserve institutional knowledge and facilitate transitions during organizational changes or upgrades.
Capability to enforce email policies, including mailbox quotas, email forwarding, and catch-all email addresses, supports operational consistency. Integration with tools supporting caldav/carddav protocols enables seamless scheduling and contact synchronization, further enhancing daily business operations.
How Email Hosting Servers Work
Email hosting servers operate through a coordinated series of functions encompassing the reception, processing, and delivery of emails. When an email is sent, the outbound mail server employs the SMTP protocol to transfer the message to the recipient’s inbound mail server, guided by MX records in the DNS to identify the correct destination server. The mail transfer agent (such as Postfix or Exim) facilitates this handoff efficiently.
Upon arrival, the mail delivery agent directs the message into the recipient mailbox. Clients then retrieve email via IMAP or POP3, depending on synchronization needs; IMAP supports server-side mailbox storage with real-time synchronization, while POP3 downloads emails locally.
Spam filtering mechanisms operate at multiple levels, often augmented by blackhole spam traps to identify and eliminate unwanted messages before reaching users. Email encryption via SSL certificates, TLS encryption, and email authentication protocols such as DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), SPF (Sender Policy Framework), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) fortify email security by verifying sender authenticity and safeguarding message integrity during mail routing.
Additional security layers include anti-virus scanning, email quarantine for suspicious messages, and multi-factor authentication for secure login. Mail server performance monitoring and backup and redundancy practices ensure data preservation and minimal service interruptions, critical for maintaining business communication efficiency.
Types of Email Hosting Services (Shared, Dedicated, Cloud-Based)
Businesses can choose from several types of email hosting services tailored to their size, budget, and security requirements:
Shared Email Hosting
Shared hosting involves multiple organizations sharing a single physical or virtual server environment. Providers like Bluehost Email Hosting and GoDaddy Email Hosting commonly offer shared email services which include maintenance of email server software and resources. While cost-effective, shared hosting may limit mailbox storage and impose mailbox quotas to manage email bandwidth, with potential compromises on server uptime during peak loads.
Dedicated Email Servers
For organizations requiring enhanced performance, security, and customization, a dedicated email setup running on a dedicated server is ideal. These servers are exclusively devoted to a single business, providing complete control over mail server performance, mail routing policies, and email security measures. Enterprises often deploy Microsoft Exchange Server or Kerio Connect on dedicated infrastructure to enable advanced functionalities such as Outlook integration, comprehensive email archiving, and robust email authentication strategies.
Cloud Email Hosting
Cloud email hosting has emerged as a highly scalable and flexible alternative, removing the need to manage physical infrastructure. Platforms like Google Workspace, Microsoft Office 365, Amazon WorkMail, and Zoho Mail deliver cloud-based email hosting with the added advantage of automatic backups, high server uptime guarantees, and seamless email migration services. Cloud hosting supports extensive email policy enforcement, multi-factor authentication, spam filtering powered by providers such as Proofpoint and Barracuda Networks, and integrated anti-virus scanning.
Virtual private servers (VPS) blend some elements of dedicated control with cloud scalability, offering performance benefits over shared hosting without full physical server commitment.
Security Features of Email Hosting Servers
The security architecture of email hosting servers is pivotal in safeguarding sensitive business communications against threats such as phishing, malware, and unauthorized access. Comprehensive email security comprises a blend of encryption, authentication, and filtering technologies implemented at various stages of the email lifecycle.
Encryption and Authentication
TLS encryption ensures data confidentiality during transmission between servers, protecting messages from interception. SSL certificates underpin encrypted connections to webmail portals and email clients alike, assuring users of a secure channel.
Email authentication protocols like DKIM, SPF, and DMARC work synergistically to authenticate message senders and prevent email spoofing. These protocols are essential in maintaining high email deliverability rates and minimizing the risk of false positives in spam filtering systems.
Spam and Malware Protection
Leading email hosting solutions integrate sophisticated spam filtering powered by AI and heuristic analysis, often supported by blackhole spam traps to eliminate illegitimate senders. Anti-virus scanning routinely checks inbound attachments to prevent malware proliferation. Suspicious emails are isolated in email quarantine zones pending review, reducing the risk of infection.
Access and Data Protection
Multi-factor authentication adds an additional security layer beyond password protection to prevent unauthorized access. Email clients, including Microsoft Outlook, Mozilla Thunderbird, and Apple iCloud Mail, support MFA integration, thereby reinforcing endpoint security.
Backup and redundancy strategies are critical in data recovery scenarios. Providers like Rackspace Email Hosting and FastMail employ frequent backups and geographically diverse data centers to mitigate data loss from hardware failures or cyberattacks.
Email policy enforcement mechanisms regulate user behaviors to comply with organizational and legal standards. Controls over mailbox quotas prevent storage overflow, while email forwarding and catch-all email address configurations must be carefully managed to avoid data leakage.
Enterprise-Grade Solutions
Enterprise offerings such as Microsoft Exchange and IceWarp incorporate advanced security features alongside collaboration tools, including CalDAV/CardDAV support for calendars and contacts, enhancing user productivity while maintaining stringent security protocols.
Security suites from Symantec Email Security and Proofpoint provide additional layers of protection against targeted attacks and data breaches, offering analytics and threat intelligence integration.
This detailed examination highlights how pivotal email hosting servers are in achieving business communication efficiency through a blend of technical infrastructure, service models, and robust security frameworks, all orchestrated by high-performance mail server software and protocols.
Impact on Email Delivery Speed and Reliability
Email delivery speed and reliability are pivotal metrics that directly influence communication efficiency and business continuity. At the core, email server software—such as Postfix, Exim, and Microsoft Exchange Server—operate as mail transfer agents (MTA) and mail delivery agents (MDA), managing mail routing between outbound mail servers and inbound mail servers. The underlying email protocols, primarily SMTP for sending and IMAP or POP3 for retrieval, significantly affect how quickly messages transit and are accessible across devices.
Effective management of MX records within the domain name system ensures that emails are correctly routed to the intended email servers without delay. Services like Google Workspace and Zoho Mail leverage robust cloud email hosting infrastructures to optimize server uptime and mail server performance, reducing latency and increasing email deliverability. Utilizing dedicated email servers or high-performance virtual private servers (VPS) can provide businesses with greater control over bandwidth allocation, minimizing bottlenecks compared to shared email hosting environments such as GoDaddy Email Hosting or Bluehost Email Hosting.
Furthermore, integrating SMTP relay services like Mailgun or SendGrid enhances outbound mail server efficiency by offloading high-volume transactional emails to specialized platforms with scalable bandwidth. On the inbound side, advanced spam filtering, DNS-based blackhole spam traps, anti-virus scanning, and email quarantine mechanisms improve reliability by filtering malicious content and preventing service interruptions.
Integration with Business Collaboration Tools
Seamless integration with collaboration tools is increasingly vital for business productivity. Leading platforms like Microsoft Exchange Server and Google Workspace offer extensive integrations with email clients and productivity suites. For example, Microsoft Outlook, with its sophisticated Outlook integration, supports calendar syncing through CalDAV/CardDAV support and facilitates email forwarding, contact management, and seamless scheduling.
Cloud-based solutions such as Office 365 and Zoho Mail feature native connectivity with collaboration tools, including document sharing, instant messaging, and video conferencing, enhancing workflow cohesion. These platforms employ secure email protocols coupled with email authentication mechanisms like DKIM, SPF, and DMARC to safeguard interactions while preserving interoperability.
Third-party mail server software like IceWarp and SmarterMail also provide integrated groupware solutions supporting email archiving, policy enforcement, and comprehensive mailbox storage management. This integration extends beyond basic communication, fostering centralized data management and team collaboration, which are particularly advantageous in hybrid or remote work environments.
Scalability and Flexibility for Growing Businesses
As organizations expand, the scalability and flexibility of their email infrastructure become critical. Cloud email hosting services such as Amazon WorkMail and Rackspace Email Hosting excel in this domain by offering elastic scalability, accommodating fluctuating email volumes without compromising mail server performance. These providers leverage redundant inbound and outbound mail servers for load balancing, ensuring consistent server uptime even during peak periods.
Dedicated email servers may offer superior performance but can require substantial capital investment and complexity in scaling. Conversely, shared email hosting and virtual private servers deliver cost-effective, scalable solutions with customizable mailbox quotas and storage capacities. Moreover, features like email migration tools streamline transitions between platforms, facilitating growth without data loss.
Maintaining scalability is also linked to the efficient use of email bandwidth and mail routing architecture, which determines how quickly messages traverse from sender to recipient across internal and external networks. Advanced email encryption techniques such as TLS encryption coupled with SSL certificates guarantee secure scaling, enabling rapid deployment of new mailboxes without compromising security or compliance.
Cost Implications and Return on Investment
Choosing between on-premises solutions, dedicated email servers, and cloud email hosting involves careful consideration of cost implications and return on investment (ROI). While dedicated email server setups, such as Microsoft Exchange Server, entail upfront costs—in hardware, licensing, and maintenance—cloud-based solutions like Google Workspace, Zoho Mail, and FastMail offer subscription models with predictable ongoing expenses. These subscriptions typically include email security features such as multi-factor authentication, spam filtering, anti-virus scanning, and email encryption, reducing additional security expenditures.
Shared email hosting and virtual private servers provide affordable access but may involve trade-offs in performance and mailbox storage that impact long-term ROI. Investments in mail server performance improvements, such as integrating SMTP relay services (e.g., SendGrid) or employing advanced spam filtering solutions like Barracuda Networks or Proofpoint, can reduce lost productivity associated with delayed or compromised email delivery.
Furthermore, utilization of email archiving and backup and redundancy services enables compliance with retention policies while safeguarding against data loss, which can save significant costs related to legal penalties and downtime. Effective email authentication via DKIM, SPF, and DMARC reduces phishing risks, minimizing potential financial liabilities. Businesses must weigh these factors carefully to optimize total cost of ownership while sustaining a resilient email infrastructure.
Role in Ensuring Data Privacy and Compliance
Data privacy and regulatory compliance are fundamental in contemporary email management, particularly under regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Email servers must implement stringent email security measures encompassing not only spam filtering and anti-virus scanning but also end-to-end email encryption. SSL certificates combined with TLS encryption protocols safeguard data in transit, ensuring the confidentiality of messages exchanged via email clients or webmail interfaces.
Implementing email authentication protocols—including DKIM, SPF, and DMARC—mitigates email spoofing and reduces phishing attacks, enhancing overall email security posture. Systems like Microsoft Exchange and Google Workspace come with embedded tools for email policy enforcement, automated quarantining of suspicious emails, and audit trails essential for compliance audits.
Additionally, email archiving solutions capture and store communications securely, supporting data retention mandates. Multi-factor authentication, now standard in cloud email hosting platforms such as Amazon WorkMail and Zoho Mail, provides an added layer of security, limiting unauthorized access to sensitive mailboxes. Complementary services like Symantec Email Security and SolarWinds Mail Assure provide enhanced monitoring for compliance adherence and threat protection.
Email Hosting and Disaster Recovery Plans
To maintain continuous communication capabilities, robust disaster recovery plans are imperative for email hosting environments. These plans encompass backup and redundancy strategies that ensure mailboxes and configurations are preserved in the event of hardware failure, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
Cloud email hosting providers like Google Workspace and Office 365 inherently offer geographically dispersed data centers that guarantee high server uptime and rapid failover. Dedicated email server environments require explicit implementation of redundant infrastructure, including duplicated inbound and outbound mail servers and frequent backups stored offsite.
Disaster recovery also relies on effective email migration tools that enable prompt restoration or relocation of mailboxes between servers and platforms, minimizing downtime. Archiving solutions provide reliable records for data restoration and forensic analysis where necessary.
It is crucial that disaster recovery plans address the management of MX records in the domain name system, enabling rapid rerouting of email traffic to backup servers. Monitoring tools supplied by vendors such as Barracuda Networks and Proofpoint enhance visibility into mail server performance and security, facilitating timely responses to incidents.
Overall, integrating comprehensive backup methods, enforcing mailbox quotas to optimize storage, and preserving email bandwidth through efficient mail routing collectively fortify the resiliency of business email communication systems.
Comparing Popular Email Hosting Providers
Selecting the ideal email hosting provider requires a comprehensive comparison of features spanning email security, server uptime, mailbox storage, and compatibility with prevalent email protocols like SMTP, IMAP, and POP3. Leading providers such as Google Workspace, Microsoft Exchange Server (including Office 365), and Zoho Mail offer robust solutions with a mix of cloud email hosting and dedicated email server options.
Google Workspace stands out for its seamless integration with both Microsoft Outlook and native webmail clients, facilitating robust mail routing and smtp relay functions via its powerful outbound mail servers. It also supports caldav/carddav for calendar and contacts synchronization, while enforcing strict email authentication mechanisms, including DKIM, SPF, and DMARC, to boost email deliverability and enhance email security.
Microsoft Exchange Server, particularly when deployed on a virtual private server or as part of a dedicated email server solution, emphasizes robust email archiving, server uptime, and mailbox quotas. Its integration with Microsoft Outlook is a core strength, and it leverages TLS encryption and SSL certificates to secure inbound and outbound mail servers. Barracuda Networks and Proofpoint provide complementary email policy enforcement and anti-virus scanning for organizations using Exchange.
Zoho Mail caters well to small and medium businesses, offering shared email hosting with domain name system (DNS) configuration that optimally sets MX records, ensuring effective mail transfer agent and mail delivery agent operations. Its spam filtering capabilities and email encryption technologies provide essential protection against blackhole spam traps and email quarantine challenges.
Other notable providers include Amazon WorkMail, with tight integration into AWS services and a focus on email bandwidth management; Rackspace Email Hosting, notable for high mail server performance; and ProtonMail, favored for privacy-oriented email encryption using end-to-end standards.
Open-source email server software such as Postfix and Exim is often employed in custom virtual private server setups, allowing deep customization of mail transfer agents and spam filtering. SmarterMail and IceWarp offer comprehensive email policy enforcement suites, integrating multi-factor authentication and anti-virus scanning, vital for enterprises with stringent compliance demands.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Businesses frequently encounter challenges in email hosting linked to email security, deliverability, and mailbox management. One primary issue is combating spam and phishing attacks while ensuring legitimate emails reach the inbox. Implementing strong email authentication protocols—DKIM, SPF, and DMARC—is critical, as is utilizing advanced spam filtering technologies and blackhole spam traps to isolate malicious traffic effectively.
Mailbox quotas and mailbox storage limitations often hamper performance; thus, choosing a solution with flexible backup and redundancy plans ensures data durability. Email archiving and migration tools become indispensable when transitioning between services like Yahoo Mail or Apple iCloud Mail and enterprise-level platforms such as Google Workspace or Microsoft Exchange.
Managing mail server performance, particularly SMTP relay limits and email bandwidth concerns, requires fine-tuning server configurations and possibly deploying dedicated email servers to handle outbound mail at scale. Leveraging cloud email hosting can help distribute loads dynamically and maintain high server uptime.
Ensuring email security further demands enforced policy controls, including multi-factor authentication, email encryption standards such as TLS encryption, sending log data via omni-channel data flow hardware and frequent anti-virus scanning to prevent malware infiltration. Solutions from providers like Symantec Email Security, SolarWinds Mail Assure, and Barracuda Networks offer integrated quarantine environments and real-time threat intelligence.
Integration challenges with popular email clients such as Microsoft Outlook and Mozilla Thunderbird can be addressed through standard-compliant protocols IMAP and POP3, with additional support for CalDAV/CardDAV ensuring smoother synchronization of calendars and contacts.
Case Studies Demonstrating Improved Efficiency
A global financial services firm migrated from an on-premises Microsoft Exchange Server to Google Workspace, leveraging cloud email hosting to gain enhanced email deliverability and reduced administrative overhead. By configuring MX records in their domain name system and adopting DKIM, SPF, and DMARC policies, they mitigated spam and phishing risks, increasing email security and maintaining 99.9% server uptime.
A mid-sized healthcare provider switched from shared email hosting with Bluehost Email Hosting to a dedicated email server using IceWarp for better email archiving capabilities and email policy enforcement. Integration with Microsoft Outlook and mobile email clients improved user productivity, while advanced anti-virus scanning and TLS encryption ensured HIPAA compliance.
An e-commerce company implemented Mailgun’s SMTP relay services and SendGrid’s outbound mail server solutions to handle surges in transactional emails without compromising mail server performance or email bandwidth. Spam filtering through blackhole spam traps and email quarantine systems minimized false positives, enhancing overall customer communication reliability.
Future Trends in Email Hosting and Business Communication
The future of email hosting hinges on increased adoption of AI-driven spam filtering and email security analytics that proactively detect and neutralize emerging threats. Email encryption will progress beyond traditional TLS encryption and SSL certificates to incorporate quantum-resistant algorithms, ensuring long-term confidentiality.
Cloud email hosting is expected to dominate due to its scalability and resilience, augmented by advanced backup and redundancy features to minimize downtime. The rise of multi-factor authentication as a mandatory security layer across platforms like Google Workspace, Office 365, and Zoho Mail exemplifies efforts to fortify email authentication.
Emerging email protocols aim to enhance mail transfer agent efficiency, optimize mail routing, and support richer collaboration tools integrated with calendars (via CalDAV/CardDAV) and task management software. Integration between email clients, webmail portals, and enterprise communication systems (e.g., Microsoft Outlook, Horde Groupware, Zimbra) will become more seamless, driven by API connectivity and cloud infrastructure.
Furthermore, email hosting providers are focusing on sustainability by improving energy-efficient mail servers and promoting virtual private server environments to reduce the carbon footprint. The trend toward zero-trust security models, supported by real-time email policy enforcement and quarantine mechanisms managed by vendors such as Symantec Email Security and Proofpoint, will reinforce business communication integrity.
FAQs
What are the main differences between SMTP, IMAP, and POP3?
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is primarily used for sending emails from clients to servers or between servers, while IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) and POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) are used by email clients to retrieve emails from a server. IMAP synchronizes email across multiple devices, maintaining messages on the server, whereas POP3 downloads and typically deletes them from the server.
How do DKIM, SPF, and DMARC help improve email deliverability?
DKIM, SPF, and DMARC are email authentication protocols that verify the legitimacy of the sender’s domain, reducing spam and phishing. SPF specifies authorized mail servers; DKIM attaches encrypted signatures; and DMARC coordinates the enforcement of both, thereby improving email security and deliverability.
What are the benefits of using cloud email hosting over a dedicated email server?
Cloud email hosting offers scalability, automatic backup and redundancy, reduced IT overhead, and typically better server uptime compared to dedicated email servers. It is ideal for businesses requiring flexible mailbox storage and high availability without investing in physical infrastructure.
How can email encryption like TLS and SSL certificates protect my emails?
TLS encryption converts email content into a secure format during transit, preventing interception, while SSL certificates authenticate the email server’s identity to clients. Both technologies ensure emails remain confidential and protect against man-in-the-middle attacks.
What is email archiving, and why is it important?
Email archiving involves securely storing emails for long-term retention, compliance, and easy retrieval. It is essential for regulatory compliance, disaster recovery, and efficient mailbox storage management.
How do multi-factor authentication and anti-virus scanning enhance email security?
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra verification step, reducing unauthorized access risk, while anti-virus scanning detects and quarantines malware in email attachments or links. Together, they fortify defenses against cyber threats and data breaches.
Key Takeaways
- Email hosting providers vary widely in features such as mail transfer agent efficiency, server uptime, and spam filtering; leading services include Google Workspace, Microsoft Exchange, and Zoho Mail.
- Implementing email authentication protocols (DKIM, SPF, DMARC) alongside encryption methods like TLS is critical for improving email security and deliverability.
- Common email challenges such as mailbox quotas, spam, and server performance can be addressed through robust email policy enforcement and backup redundancy strategies.
- Case studies reveal that migration to cloud email hosting and use of specialized SMTP relay services improve efficiency and maintain high mail server performance.
- Future email hosting trends emphasize AI-driven security, zero-trust models, quantum-resistant encryption, and seamless integration with business communication tools.