Child Data Ransom, Hessen Encryption Report, Steganography RAT Deployment - Cybersecurity News [February 26, 2024]
We’re back again with the latest in cybersecurity news this week! Join us for a detailed look into the Rhysida ransomware and the Hessen attack to get updates on how you can stay safe. We’ll also share news of the new IDAT loader targeting the Ukrainian Armed Forces, PayPal’s new patent for browser cookie security, and Apple’s latest PQ3 encryption for iMessages. Stay tuned.
Rhysida Ransomware Demands $3.6 Million Ransom for Encrypted Children’s Data
The Rhysida ransomware gang claimed they had breached Chicago’s Lurie Children’s Hospital at the beginning of February 2024.
Following the attack, the hospital had to take down its IT systems and even postpone medical care for select individuals, as the breach impacted email, phone, MyCharts, and on-premises Internet. The breach also affected Ultrasound and CT scan results, which were unavailable, and doctors had to resort to pen and paper prescriptions.
This week, Rhysida added Lurie Children’s Hospital to its extortion portal and has claimed they have access to 600 GB of hospital data, which they’re selling for 60 BTC to a single buyer. They also added a deadline of 7 days, after which it would be sold to multiple threat actors.
Lurie Children’s Hospital has not released an update since February 23, 2024, when it shared news of an ongoing effort to restore its IT systems. If you’re a patient, you should carry a printed insurance card for your appointments and your children’s medication bottles.
Currently, some systems are online, but the health record systems and MyChart are still offline. So are the payment systems – the timeframe has been extended as long as the outage persists.
Hessen Consumer Center Reports Encryption of Its Systems by Ransomware
The Hessen Consumer Center in Germany was the victim of a ransomware attack that shut down all IT systems and disrupted their availability.
Hessen has over 6 million people, and its Consumer Center is a non-profit that advises state residents regarding consumer law, finance, insurance, Internet, energy saving, healthcare, telephone, food, and more.
The organization shared an announcement detailing how it suffered an attack on its IT infrastructure and how communication would be disrupted. Most things have been addressed, and the website is fully operational, but people still face trouble connecting to the organization. Little detail was shared about the ransomware attack, but the data of the citizens of Hessen might be at risk.
The state’s data protection and IT security offices were investigating the incident when its responsibility was claimed by the Blackcat ransomware gang, along with data samples on the gang’s dark web extortion page.
The occurrence of such attacks emphasizes the importance of implementing ransomware protection measures, which will assist in ensuring your continued security.
IDAT Loader’s Latest Version Deploys Steganography to Deliver Remcos RAT
A new hacker group has been delivering the Remcos RAT (Remote Access Trojan) using steganography to an entity in Finland operated by Ukraine.
The threat actor group is being tracked as “UAC-0184” and has been carrying out attacks against the Ukrainian Armed Forces since 2023. Morphisec spotted their latest activity and has shed light on their latest attack methods.
Steganography is a rare tactic where threat actors encode malicious code into the pixels of images to avoid detection. Since the payload chunks are small, they do not result in an altered image but might distort it. The threat actors start a chain attack with a phishing email, posing as Ukrainian or Israeli Defense, and trick innocent victims into opening short file attachments with an infection chain.
The chain launches an executable that activates a malware loader called “IDAT”. It’s a modular loader that can inject code and execution modules as well. Furthermore, to avoid detection, the API (Application Programming Interface) calls are not written in plaintext but resolved at runtime with the help of a decryption key.
IDAT executes the Remcos RAT at the final stage, which the threat actors can use for data exfiltration and activity monitoring. You can find more details on Ukraine’s state website.
PayPal Seeks Patent for Innovative Technique to Identify Pilfered Cookies
PayPal filed a patent this week for a new method that will identify when a super-cookie is stolen.
If such an event is identified, it can help improve cookie-based authentication and limit account takeovers. Super-cookies are LSOs (Local Shared Objects) injected into the network as UIDHs (Unique Identifier Headers) instead of standard cookies stored locally.
The super-cookies allow cross-site tracking and can follow multiple browsers on the same system, collecting all browsing activity. They’re challenging to detect and wipe as they’re not local. Still, PayPal has identified a new method to calculate a fraud risk score in its authentication mechanism to identify fraudulent logins on its platform.
Whenever a system gets an authentication request, it identifies the cookie storage locations and sorts them (based on the fraud risk they pose). Then, the system assesses the risk score by comparing expected values with those assigned and manages the authentication accordingly. Also, the cookie values retrieved are encrypted using public key cryptography.
PayPal’s patent application, incorporating phishing protection, has the potential to fortify defenses against cyber threats. It was published a few days ago, but they filed it back in July 2022 under “Super-Cookie Identification for Stolen Cookie Detection.”
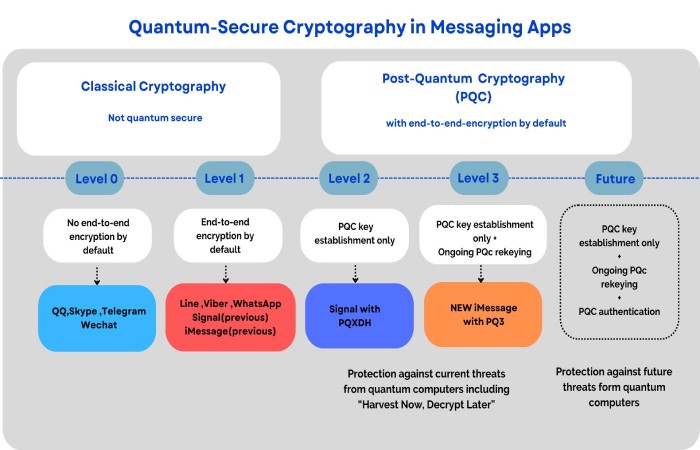
Apple Introduces PQ3 Quantum-Resistant Encryption to iMessage
Apple is adding a PQ3 protocol to its iMessages to defend its encryption against quantum attacks.
PQ3 is a post-quantum cryptographic protocol that will enhance iMessage’s E2EE (end-to-end encryption). Quantum computing threatens messaging applications because it can crack algorithms instantly, and applications like Signal have also strengthened their offerings by adding NIST-approved algorithms for quantum-resistance.
Apple shared how the PQ3 is the most substantial security in any at-scale messaging protocol in the world but has not swapped its pre-existing ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography). It has adopted a hybrid model combining both protocols for robust defense. PQ3 uses the Kyber algorithm and has a periodic post-quantum rekeying mechanism, the first of its kind for messaging applications.
The new algorithm will bring high security to its application and a large consumer base. It’s a significant development because it will set an industry standard for competitors to follow.