Here is the latest weekly cybersecurity bulletin, with the latest cybersecurity news and feature announcements.
BlackCat Ransomware Attacks Exploit Malicious Windows Kernel Drivers
The BlackCat ransomware group (ALPHV) has been employing signed malicious Windows kernel drivers in their latest attacks to evade detection.
Trend Micro observed an improved version of the gang’s “POORTRY” malware which was also observed in multiple ransomware attacks last year. Threat actors tried using a Microsoft-signed POORTRY driver that kept getting detected, leading to this improved one, which uses a stolen or leaked cross-signing certificate and helps the ransomware gang elevate privileges on compromised machines and stop all security agent processing activities.
It is recommended that Windows users enable the “Driver Signature Enforcement” feature to protect their systems.
Thousands of Victims Defrauded by Crypto Phishing Service, Inferno Drainer
Inferno Drainer, a new crypto phishing and scam, duped 4,888 victims, stealing nearly $5.9 million in crypto.
Scam Sniffer, a Web 3.0 anti-scam enterprise, reported that the Inferno Drainer phishing service has over 689 fake websites that came online after March 2023. These websites target 220 famous brands, promoting multichain fraud and Aaven and Art Blocks draining.
The malicious actors behind the toolkit provide a modern admin panel with customizations and trials, with the users paying the threat actors who developed Inferno Drainer 20% of all proceeds. The cut for the threat actor increases for extra phishing site creations. Out of the millions of assets, the most significant amount was stolen from Mainnet at $4.3 million, followed by Arbitrum, Polygon, and BNB.
Individuals must stay vigilant while making crypto transactions and avoid disclosing personal information.
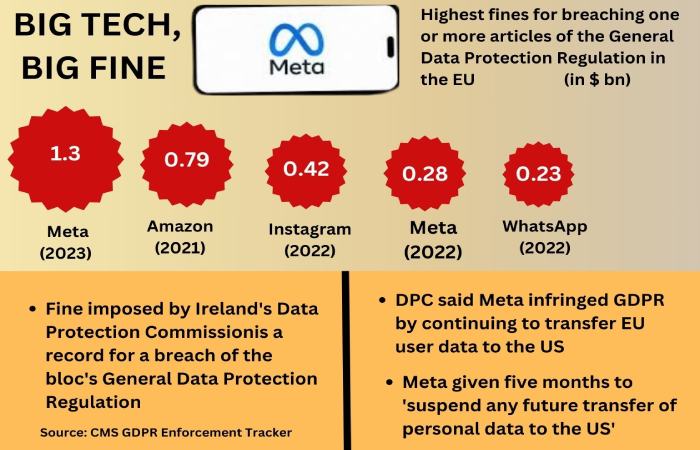
Meta Fined $1.3 Billion by E.U. for Transferring Data to U.S. Servers
The Irish DPC (Data Protection Commission) has fined Meta $1.3 billion based on Article 46(1) of GDPR.
Meta’s application, Facebook, transfers the data of EU-based citizens to the U.S., where data protection regulations are different for all states and inadequate to protect E.U. citizens’ rights.
The article from the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) forbids the transfer of personal data to countries or regions that do not have adequate legal remediation mechanisms and do not warrant safety. As a result, the DPC imposed a $1.3 billion fine on Meta and has requested that all data transfers be suspended within five months.
Meta will also have to stop processing and holding data transferred illegally to the U.S. within six months.
Inactive for Over 2 Years? Google Will Delete Your Accounts
Google announced that it had updated its personal account policy and will deactivate accounts that have been inactive for over two years.
After the maximum period of 2 years, the accounts containing all content, settings, saved data, and more may be deleted. The account deletion policy will apply to all Google services like Gmail, Drive, Meet, Docs, Photos, YouTube, and more.
The new policy will not apply to organizational accounts or businesses. The new policy aims to boost online security as inactive accounts may face cyber threats. The new policy has taken effect, and Google will start deleting accounts from December 2023.
For users looking to save their accounts from inactivity, Google recommends reading or sending an email, using Google Drive, watching a YouTube video, downloading apps, using Google Search, or merely signing in to a third-party app using the account.
Clop Ransomware Attacks Linked to Return of Notorious FIN7 Hackers, Says Microsoft
FIN7, a financially motivated threat actor group, has been linked to the deployment of Clop ransomware payloads.
Microsoft highlighted the new threat in a Twitter thread. FIN7 has been around since late 2021, but its recent deployment of clop ransomware saw a PowerShell-based POWERTRASH malware dropper that works from memory.
It also drops a post-exploitation tool that allows the threat actors to maintain a foothold on the target network, move laterally, and deploy the Clop ransomware using OpenSSH. This strain is the newest one FIN7 is using, as the threat actor gang has also used REvil and Maze ransomware before.
Individuals and organizations should be on guard and practice protective measures to stay safe.
Bug Bounty Program for Android Applications Launched by Google
Google also launched a new bug bounty program called the Mobile VRP (Vulnerability Rewards Program) that will reward security researchers for the flaws they find in Android applications.
Google released the VRP with the primary goal of speeding up the process of taking care of vulnerabilities and flaws in its first-party Android applications. The qualifying vulnerabilities include ACE (Arbitrary Code Execution), theft of sensitive and chained weaknesses such as orphaned permissions, zip path flaws, or intent redirections that the threat actors can exploit.
Google will reward up to $30,000 for the ACE flaws and up to $7,500 for bugs that threat actors can exploit to steal data remotely.