Here’s the Weekly Cybersecurity Bulletin to keep you updated with the latest cybersecurity developments.
CISA Directs Federal Agencies to Enhance the Security of Internet-Exposed Network Devices
CISA (Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency) has issued a binding operational directive, BOD 23-02, ordering federal civilian agencies to secure misconfigured or Internet-exposed networking equipment.
This directive applies to routers, firewalls, proxies, and load balancers, granting authorized users access to network administrative tasks. CISA emphasizes reducing the attack surface caused by insecure or misconfigured management interfaces, and agencies must remove these interfaces from Internet exposure or protect them with separate policy enforcement points.
CISA will provide technical expertise and assist in remediation. The compliance reports will be submitted to the Director of the Office of Management and Budget and the Department of Homeland Security.
CISA plans to update the directive in two years. Additionally, it has launched the Ransomware Vulnerability Warning Pilot program for critical infrastructure organizations.
Extensive Phishing Campaign Utilizes 6,000 Websites to Mimic 100 Brands
Since June 2022, a widespread brand impersonation campaign has targeted over a hundred popular apparel, footwear, and clothing brands.
The campaign tricks users into sharing their account credentials and financial information on fake websites. Brands such as Nike, Caterpillar, Puma, Vans, Adidas, and others have been impersonated by over 6,000 sites using a pattern of brand name plus location followed by “.com.”
The campaign displayed a significant surge in activity between January and February 2023, with 300 new fake sites emerging monthly. Researchers discovered that the domains, hosted by Packet Exchange Limited and Global Colocation Limited, had been in operation for up to two years.
These malicious domains have even been indexed by Google Search, giving them a higher ranking and appearing credible to users. The scam websites may not deliver purchased products or send counterfeit items while potentially storing credit card details for selling to malicious actors.
Users should avoid promoted search results and verify brand websites through trusted sources.
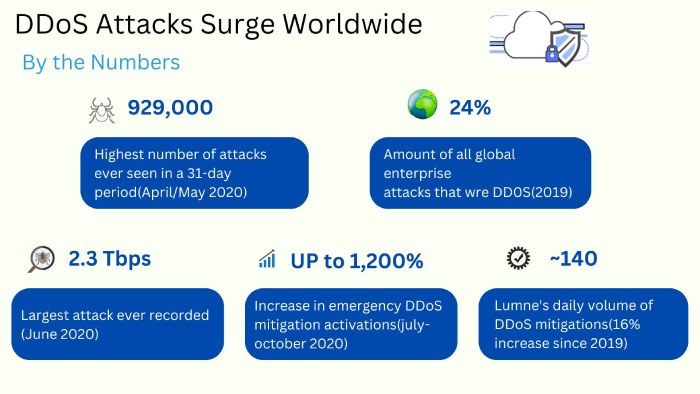
Ongoing DDoS Attacks and Data Leak Alert Issued by Swiss Government
The Swiss government has faced a series of cyber threats recently. It was revealed that a ransomware attack on IT supplier Xplain, affecting various government departments and even the military, may have exposed sensitive data.
The Play ransomware gang breached Xplain on May 23, 2023, and published the stolen data on June 1 after their extortion attempts failed. The Swiss government is investigating the extent of the data breach and the specific units affected.
Additionally, the government is now dealing with distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks by the pro-Russian hacktivist group NoName. These attacks have caused access issues to several Federal Administration websites and online services. NoName has been targeting NATO-aligned countries, Europe, Ukraine, and North America, since early 2022.
Furthermore, NoName targeted the parliament website during discussions on Switzerland’s neutrality and potential aid to Ukraine.
Service Provider for Russian Banks Disrupted by Ukrainian Threat Actors
The Ukrainian malicious group Cyber.Anarchy.Squad has claimed responsibility for an attack that brought down Russian telecom provider JSC Infotel8.
Based in Moscow, Infotel provides connectivity services to the Russian Central Bank, other Russian banks, online stores, and credit institutions. As a result of the attack, central banks in Russia lost access to the country’s banking systems, preventing them from making online payments.
Infotel confirmed the incident on its website, stating that it is working on restoring its damaged systems. The Ukrainian adversaries released screenshots of their access to Infotel’s network, including a network diagram and a compromised email account.
This malicious group has previously targeted Russian organizations and leaked stolen employee and customer information databases.
Australian Commercial Law Giant Successfully Thwarts BlackCat Ransomware Extortion Attempt
Australian law firm HWL Ebsworth has confirmed that the AlphV ransomware gang, also known as BlackCat, targeted it in a cyberattack.
The law firm, one of Australia’s largest, suffered a data breach, with the threat actors leaking 1.45 terabytes of data containing over a million documents allegedly stolen from their systems in April 2023. The gang has threatened to release more data if their demands are unmet.
Despite the threat, HWL Ebsworth has stated that they will not give in to the extortion demands, prioritizing their ethical and moral duties. The leaked documents raise concerns about exposing sensitive or confidential information, potentially impacting clients such as ANZ banking groups and various government entities.
The indexed database on BlackCat’s site allows easy exploration of the leaked documents, posing additional risks.
Enhanced Safeguards Introduced for Your Credentials in Google Chrome Password Manager
Google Chrome is introducing new security features for its built-in Password Manager to enhance user safety and protect against account hijacking attacks.
The Password Manager, an integral part of Google’s services, enables users to manage and autofill credentials across various apps. While storing credentials on the browser can pose risks, following sound security practices minimizes concerns.
Google has announced five new features to bolster Password Manager security. These include a dedicated desktop shortcut for easy access, biometric authentication on the desktop, saving custom notes with login credentials, importing passwords from other managers, and Password Checkup for flagging weak and reused passwords on the mobile iOS app.
These features aim to enhance user account safety in an environment where storing passwords in browsers carries inherent risks.