Email remains the primary attack vector for phishing and business email compromise, making DMARC a critical layer of protection for modern organizations. For MSPs and service providers, conducting a thorough DMARC audit is no longer optional it’s essential for protecting client domains, improving email deliverability, and ensuring proper SPF and DKIM alignment.
This guide breaks down the ultimate DMARC audit process for businesses, with a focus on reporting, policy enforcement, and alignment strategies. Whether you’re onboarding a new client or strengthening an existing security stack, you’ll learn how to identify gaps, interpret aggregate reports, and move domains toward full DMARC enforcement with confidence.
Why DMARC audits matter for MSPs: business outcomes, risk reduction, and client value
Business outcomes and client value
A rigorous DMARC audit helps MSPs translate technical email authentication into measurable business outcomes: fewer phishing incidents, stronger domain protection, and improved email deliverability for every business email stream. By validating the DMARC record across each domain and subdomain, you surface misconfigurations before they cause deliverability issues or brand damage. This drives policy enforcement with confidence and supports compliance regulations and business compliance mandates that increasingly require domain-based message authentication, reporting, and conformance.
Company reputation and domain protection
- Company reputation and domain reputation both improve when email spoofing declines. Phishing protection is not only a control objective but a brand safeguard.
- Major receivers like Google, Yahoo, and Microsoft factor conformance, SPF alignment, DKIM alignment, and consistent DMARC policy into sender requirements and risk levels.
- An MSP that operationalizes monitoring and domain monitoring elevates client trust and wins recurring managed services by preventing abuse and tightening policy distribution.
Risk reduction and phishing protection
A DMARC audit anchored in DNS configuration, domain inspection, and diagnostic checks reduces security risk level by identifying gaps in SPF and DKIM authentication mechanisms. It detects Relay usage, unauthorized senders, and syntax errors in the TXT record. With record parsing of aggregate reports and forensic reporting, MSPs perform risk assessment across all sources, then move from a none policy to a quarantine policy and ultimately a reject policy as conformance improves. This staged enforcement sharply cuts email spoofing while preserving email program visibility.
Email deliverability and conformance benefits
Alignment-led conformance enhances deliverability, as receivers reward authenticated flows. Consistent DMARC policy value (authorized values for p=) plus protocol enhancements like sub-domain policy (sp=) and optional tags (fo, ri) improve reporting and enforcement predictability. By tightening validation and configuration, MSPs help clients satisfy evolving sender requirements from large ISPs and reduce false positives that can create deliverability issues.
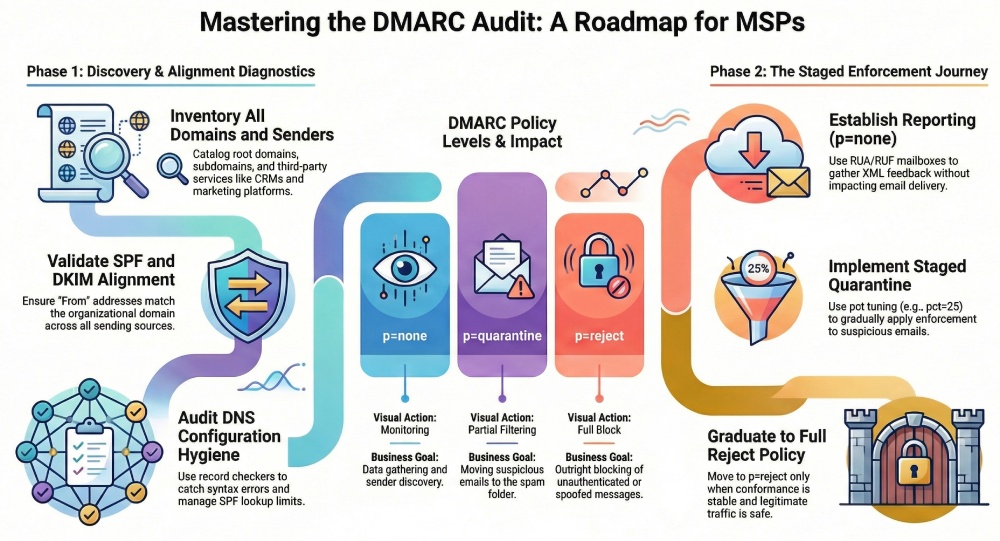
Audit preparation and scope: domain inventory, sender catalog, DNS baselining, and stakeholder roles
Domain inventory and domain inspection
Start with a complete inventory: root domains, parked domains, and all sending subdomains. Perform domain lookup and domain inspection to confirm the presence of a DMARC record, SPF (Sender Policy Framework), and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) for each. Verify DNS configuration health, confirm the TXT record location (dmarc.POLICYDOMAIN), and note PARENT_POLICY inheritance behavior used by some tools and parsers.
DNS configuration baseline and record syntax checks
- Validate record syntax with a record checker from MXToolbox, DMARC Inspector, dmarcian, or EasyDMARC. Catch syntax errors, authorized values, and record syntax mistakes early.
- Document optional tags (rua, ruf, fo, ri, sp) and the reporting interval to set expectations for XML feedback volume.
- Establish blacklist monitoring to correlate domain reputation shifts with enforcement changes.
Sender catalog and Relay mapping
Create a sender catalog of all platforms that Relay: marketing automation, CRM, ERP, billing, support, and third-party services. Map each to authentication mechanisms and alignment strategy (SPF vs DKIM). This catalog is essential to setup and management of policy enforcement, ensuring each sender implements DKIM keys, SPF includes, or custom routing as needed to meet conformance without breaking legitimate traffic.
Stakeholder roles and managed services governance
Define stakeholder roles: DNS owners for configuration, mail admins for enforcement, security for risk assessment, and legal/compliance for policy distribution and business compliance alignment. In a managed services model, document escalation paths, risk levels, and approval criteria to move from none policy to stricter modes. Reference RFC 7489 when clarifying policy value and sender requirements across teams.
DMARC reporting setup and normalization: RUA/RUF mailboxes, parsers, privacy, and data retention
RUA/RUF mailboxes, privacy, and data retention
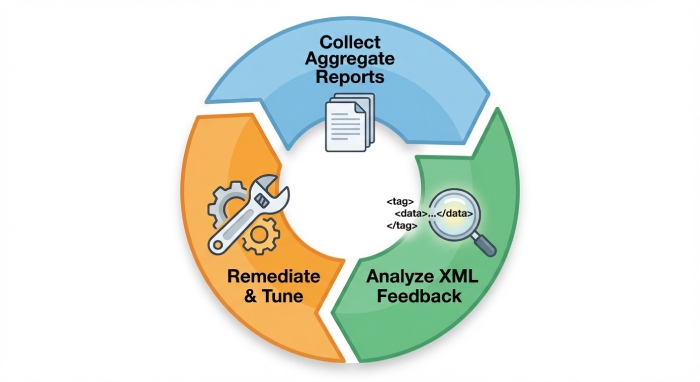
Create dedicated RUA (aggregate reports) and RUF (forensic reporting) mailboxes with retention policies. Apply privacy controls when handling forensic data, and define a reporting interval that balances insight with volume. Normalize XML feedback across providers to capture conformance, policy enforcement outcomes, and sources generating email spoofing attempts.
Aggregate reports and forensic reporting parsing
- Use record parsing pipelines to standardize differing XML feedback formats, noting policy value, source IPs, domain alignment, and authentication results per source.
- Flag diagnostic checks that show partial alignment or intermittent failures, then route to remediation workflows.
- Ensure validation steps cover both SPF and DKIM results and the resulting DMARC policy action taken by receivers.
Parsers, tools, and normalization pipelines
Adopt parsers and dashboards from vendors such as DMARC Inspector, dmarcian, EasyDMARC, and MXToolbox. Many offer a record wizard, record checker, and dashboards vetted on G2 Crowd, SourceForge, Expert Insights, and Channel Program. Standardize taxonomy so internal metrics align with policy enforcement states (none policy, quarantine policy, reject policy) and capture conformance deltas by domain and sender.
Tooling notes and configuration hygiene
- Document POLICYDOMAIN conventions and any PARENTPOLICY inheritance logic used in tools.
- Track configuration drift in DNS configuration, DKIM key rotation, and SPF include chains.
- Integrate monitoring with SIEMs to correlate phishing protection events with DMARC audit findings.
Metrics, reporting interval, and monitoring
Define KPIs: percentage of aligned volume, SPF alignment rate, DKIM alignment rate, unknown senders, and enforcement coverage by domain. Use domain monitoring to catch regressions. Schedule reviews at a set reporting interval (e.g., daily aggregates, weekly risk assessment) and communicate progress to stakeholders. This cadence sustains email security momentum and keeps policy distribution aligned to business objectives.
For broader strategy and services that complement email authentication, many MSPs consult resources dedicated to email security, such as email security.
Alignment fundamentals and diagnostics: SPF/DKIM identifiers, relaxed vs strict, and measuring alignment at scale
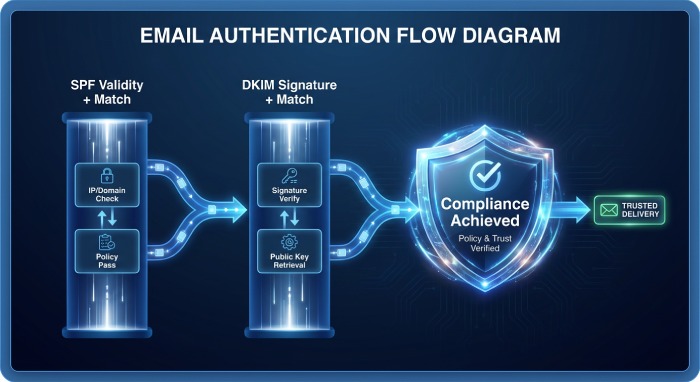
SPF, DKIM, and domain-based message authentication
DMARC (domain-based message authentication, reporting, and conformance) evaluates alignment across SPF and DKIM. SPF checks the SMTP envelope domain against the DMARC policy’s domain; DKIM checks the d= domain in the signature. Where either aligns and passes validation, the message satisfies DMARC conformance and is protected from policy enforcement actions, improving phishing protection and minimizing email spoofing risk across business email flows.
Relaxed vs strict, sub-domain policy, and PARENTPOLICY
- Relaxed alignment allows organizational-domain matches; strict requires exact domain matches. Choose based on sender landscape and risk levels.
- Use sub-domain policy (sp=) to set enforcement for child domains; document any inherited logic akin to PARENTPOLICY used by tooling to visualize policy distribution.
- Adjust policy value gradually as you validate alignment across all senders.
Measuring alignment at scale and diagnostic checks
At scale, conformance depends on disciplined diagnostics:
- Track SPF alignment and DKIM alignment rates per sender and domain via aggregate reports.
- Investigate failures with diagnostic checks: DNS lookup limits in SPF, DKIM key mismatches, or misrouted Relay paths.
- Resolve deliverability issues caused by misaligned Return-Path or From domains via configuration updates and validation, not just temporary enforcement exceptions.
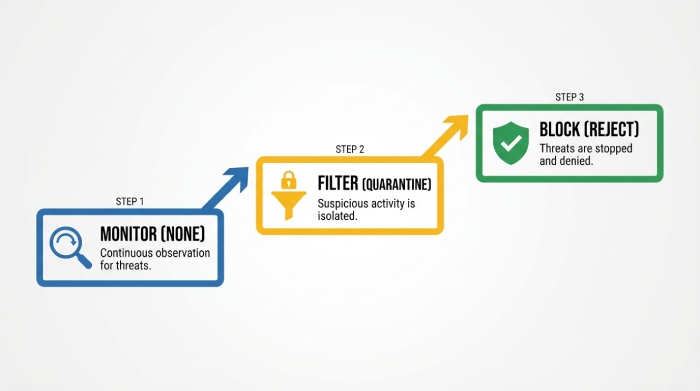
From none policy to quarantine policy to reject policy
A mature DMARC audit roadmap advances enforcement in stages:
- Start with a none policy to build a complete picture from reporting while you remediate gaps.
- Move to a quarantine policy for partial enforcement once aligned volume is high and residual risk assessment is acceptable.
- Graduate to a reject policy when conformance is sustained, sender requirements are fully met, and blacklist monitoring plus domain reputation trends are stable.
Throughout, maintain setup and management discipline: keep TXT record entries clean, avoid SPF DNS-mechanism bloat, rotate DKIM keys, and document protocol enhancements. Ensure policy value and optional tags are explicit and consistent. By iterating on domain inspection, DNS configuration hygiene, and tooling insight, MSPs can deliver durable policy enforcement that strengthens phishing protection, defeats email spoofing, and elevates client outcomes through resilient email authentication.
Third-Party and SaaS Sender Remediation
Cataloging External Senders with a Structured DMARC audit
A thorough DMARC audit is the fastest way to inventory every third-party platform that sends business email on your behalf. Begin with domain inspection and domain lookup across your POLICY_DOMAIN and known subdomains to enumerate active SMTP Relay paths, marketing platforms, CRM systems, and ticketing tools. Aggregate reports and XML feedback quickly reveal which sources pass or fail email authentication, enabling precise risk assessment and prioritization by security risk level and risk levels.
Perform diagnostic checks with tools such as DMARC Inspector, dmarcian, EasyDMARC, and MXToolbox to validate DNS configuration for SPF and DKIM and to spot syntax errors in the DMARC record. These platforms offer record checker utilities, record parsing of the TXT record, and enforcement simulations that highlight deliverability issues before you change policy value or policy distribution. Reference RFC 7489 and related protocol enhancements to ensure authorized values and record syntax remain compliant with Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM).
DKIM Keys and SPF Includes Hygiene
For third-party and SaaS senders, configure sender requirements up front: publish provider-managed DKIM keys with strong lengths and rotate them regularly; audit SPF includes to keep the mechanism chain short and under 10 DNS lookups. Maintain SPF alignment by matching the RFC5321.MailFrom or RFC5322.From with the organizational domain, and ensure DKIM alignment by signing with a d= domain that aligns to the POLICY_DOMAIN. Use domain monitoring to track domain reputation and blacklist monitoring after key or include changes to protect company reputation and domain protection.
When adding providers, confirm their guidance against compliance regulations and business compliance controls. Many vendors provide a record wizard for quick setup and management, but always review the configuration to avoid accidental policy enforcement conflicts or misapplied optional tags such as ri= (reporting interval).
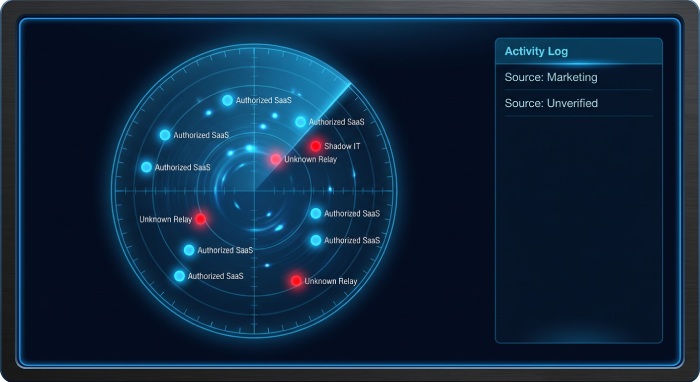
Envelope/Bounce Domains and Shadow IT Discovery
Indirect mail paths—especially when envelope/bounce domains differ from visible From can break alignment and conformance. Investigate Return-Path domains, SMTP relays, and forwarding services that re-envelope messages, and map them to legitimate SaaS sources. Shadow IT emerges when teams deploy new tools without central DNS configuration; continuous DMARC audit cycles, domain inspection, and domain monitoring will surface unauthorized senders, preventing email spoofing opportunities and preserving phishing protection.
Practical Remediation Steps
- Validate every third-party with DKIM alignment tests and SPF alignment checks.
- Assign a sub-domain policy (sp=) to segment experiments on a delegated subdomain.
- Use record parsing to confirm policy value, optional tags, and record syntax prior to rollout.
Interpreting Aggregate Data and Failure Modes
Reading Aggregate Reports and XML Feedback
Aggregate reports drive reporting clarity: they quantify pass/fail by source IP, envelope domain, and alignment, forming the backbone of conformance measurement. Parse XML feedback daily or at the chosen reporting interval to identify authentication mechanisms that need remediation. Correlate changes in DMARC policy to fluctuations in email deliverability, and escalate senders with recurring failures for validation and enforcement planning.
Forwarding, Indirect Mail, and ARC
Forwarding and indirect delivery through list servers or security gateways can break DKIM or SPF due to header or path modifications. Authenticated Received Chain (ARC) provides protocol enhancements to preserve authentication context through intermediaries. When conformance is impacted by forwarding, prefer DKIM as the primary authentication method, encourage providers to sign, and document exceptions in your incident playbooks to avoid unnecessary quarantine policy triggers.
Spoof Campaign Detection and Conformance Metrics
Spikes in DMARC reporting for unauthorized sources or abnormal failure modes often signal active email spoofing. Monitor patterns across providers like Google, Yahoo, and Microsoft to understand how receiver enforcement may affect business email. Combine aggregate reports with forensic reporting (where permitted) to pinpoint attack domains, source networks, and campaigns, then tighten policy enforcement on the affected POLICY_DOMAIN or a targeted subdomain for immediate phishing protection.
Policy Design and Safe Rollout
From none policy to quarantine policy to reject policy
Design a staged DMARC policy that balances risk and email program visibility. Start with a none policy to gather data while avoiding disruptions, then transition to a partial quarantine policy with pct tuning (for example, pct=25, 50, 75) to measure enforcement impact. Once conformance is proven and deliverability issues are addressed, graduate to a full reject policy to maximize domain protection and policy enforcement against spoofing.
Alignment Modes, sp/adkim/aspf, and Subdomain Strategy
For precise control, define adkim and aspf alignment modes (r/relaxed vs s/strict) to match your sender ecosystem. Set sp= to establish a sub-domain policy that may differ from the PARENTPOLICY, allowing stricter enforcement on marketing subdomains or more lenient settings during onboarding phases. Explicitly document sender requirements for alignment and list POLICYDOMAIN constraints per business unit to keep configuration consistent across teams.
pct Tuning and Policy Distribution Details
- Use pct to gradually scale enforcement and reduce risk across large mail volumes.
- Plan policy distribution windows that align with marketing calendars to prevent unintended impact.
- Version-control the DMARC record, including TXT record comments where allowed, to track setup and management decisions.
Ongoing Operations: Monitoring, Alerting, and Response
Monitoring, Alerting, and KPIs
Sustain policy enforcement with continuous monitoring. Track KPIs such as aligned volume, failure rates by mechanism, conformance trend, and spoofed block rates to quantify email security outcomes. Implement alerting on security risk level thresholds for instance, spikes in unauthenticated traffic or sudden DKIM key usage drops using SIEM correlation and domain monitoring to trigger timely diagnostic checks.
Incident Response Playbooks and Client Communications
Develop incident response playbooks that define triage for aggregate failure surges, forensic reporting review, blacklist monitoring steps, and remediation tasks (key rotation, SPF include updates). Communicate proactively with stakeholders and clients about enforcement milestones, risk assessment results, and any temporary policy value adjustments that affect email deliverability. Clear client communications build trust, ensure business compliance, and maintain company reputation while you iterate toward full conformance.
Escalation Thresholds and Governance
- Set authorized values and escalation paths for changing none policy to a stricter stance.
- Require change control for DNS configuration edits to SPF, DKIM, and the DMARC record.
Scaling for MSPs and Large Enterprises
Automation, DNS as Code, and SIEM/SOAR Integrations
For MSPs and large programs, automation ensures consistency across tenants. Manage DNS as code to templatize TXT record updates, enforce record syntax linting, and prevent syntax errors before production. Integrate reporting into SIEM/SOAR to correlate aggregate reports, XML feedback, and blacklist monitoring with broader security signals, enabling faster enforcement actions and measurable conformance gains.
Multi-Tenant Dashboards, Access Controls, and Managed Services
Adopt multi-tenant dashboards from providers validated on G2 Crowd, SourceForge, Expert Insights, or Channel Program to streamline setup and management. Implement role-based access controls for record checker tools, record wizard workflows, and domain lookup utilities. For managed services offerings, standardize runbooks for validation, configuration, and policy enforcement, and include periodic risk assessment briefings that demonstrate phishing protection impact and adherence to compliance regulations.
To support holistic email security, align operational controls with authentication mechanisms and continuously verify that Sender Policy Framework and DomainKeys Identified Mail are functioning across every Relay and provider ecosystem.
FAQs
What is the safest path from p=none to full enforcement?
Begin with a none policy for visibility, fix alignment and failure sources, then apply pct tuning on a quarantine policy before moving to a full reject policy. Measure conformance and email deliverability at each step to avoid disrupting legitimate business email.
How do forwarding and mailing lists affect DMARC outcomes?
Forwarders and lists can break SPF and sometimes DKIM, reducing conformance and triggering enforcement actions. ARC helps preserve authentication context; prioritizing DKIM signing and monitoring aggregate reports minimizes false failures.
Which tools help validate my DMARC record and DNS configuration?
Platforms such as DMARC Inspector, dmarcian, EasyDMARC, and MXToolbox offer record parsing, record checker features, and diagnostic checks. They help spot syntax errors, confirm authorized values, and validate TXT record updates against RFC 7489.
How should MSPs manage multi-tenant policy enforcement at scale?
Use automation and DNS as code to standardize configuration, and integrate reporting with SIEM/SOAR for unified monitoring. Employ access controls and multi-tenant dashboards to coordinate enforcement, domain inspection, and client communications.
Key Takeaways
- Use a structured DMARC audit and domain inspection to discover all senders, remediate SPF/DKIM alignment, and build an accurate inventory.
- Roll out DMARC policy safely: start with none policy, use pct tuning on quarantine policy, then finalize with reject policy when conformance is stable.
- Leverage aggregate reports, XML feedback, and ARC to interpret failure modes, reduce false failures, and detect email spoofing campaigns.
- Operationalize monitoring, KPIs, and incident playbooks to sustain policy enforcement and phishing protection without harming email deliverability.
- For MSP scale, automate DNS configuration as code, integrate with SIEM/SOAR, and use multi-tenant dashboards to manage access and reporting.