Gmail security requirements for brands and businesses
Gmail is one of the best email service providers in the world. Gmail has managed to beat all the competition because of its state-of-the-art features and seamless integration with other Google services. With a whopping user base of 1.8 billion, Gmail focuses extensively on security requirements and restrictions in order to enhance user safety and data privacy.
This article explores the various security requirements of Gmail, walks you through the nuances of these requirements for your business email domain, and also helps you gain an understanding of how to start with or maintain the Gmail security requirements.
Sender authentication
If you are planning to send bulk emails on Gmail, then you are required to conform to the following:
- SPF or Sender Policy Framework
- DKIM or DomainKeys Identified Mail
- DMARC or Domain-based Messages Authentication Reporting and Conformance
Let’s understand each protocol one by one:
SPF
The oldest email authentication protocol, SPF, is designed to ensure that unauthorized emails sent from your domain don’t land in the targeted recipients’ inboxes. Deploying SPF keeps your email communications safe from threat attempts such as spoofing and phishing.
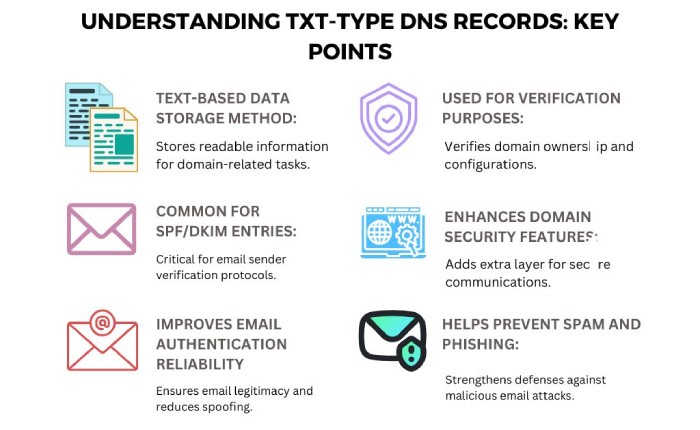
As a domain owner, you can create a list of authorized servers that are allowed to be used to send emails from your domain. The list is uploaded as a TXT-type DNS record. When a recipient’s email server receives an email, it retrieves the list of authorized servers to check whether or not the sending server is a part of the approved list.
In case the sender’s server is not authorized, the email either gets rejected or is moved to the spam folder.
DKIM
DKIM is used by the domain owner to ensure that the outgoing emails are not getting tampered with during transit. To do this, DKIM uses cryptographic signatures. These signatures are added to DKIM protocol headers. A pair of public and private keys are generated by the domain owner. The public key is uploaded to the DNS records so the recipient server can retrieve it.
After retrieving it, the recipient server uses the same to decrypt the cryptographic signature. The email passes the DKIM check when the contents of the email match the decrypted signature.
When an email passes the DKIM check, the result shows as ‘pass.’ However, if the content doesn’t match the cryptographic signature or the signature itself is missing, the result is shown as ‘fail.’
Another benefit of using the DKIM protocol is enhanced email deliverability. Emails that contain DKIM signatures are less likely to land in the spam folder.
DMARC
The latest of the three email authentication protocols, DMARC, operates on the basis of SPF and DKIM results. DMARC enables domain owners to publish one of the policies (none, quarantine, or reject), based on which the recipient email servers can decide how to tackle the unauthorized emails sent from your domain.
In order to pass the DMARC check, the ‘From’ address of an email must align with the domain used in DKIM and SPF checks. However, if an email fails the DMARC check, the recipient server tackles it as per one of the three policies mentioned above. Domain owners instruct the recipient servers as to how to handle unauthorized emails. The recipient server can either take no action and let the email land safely in the inbox (p=none), send it to the spam folder (p=quarantine), or bounce it back to the sender (p=reject).
DMARC also comes equipped with a reporting feature that allows the domain owners to study the unauthorized emails closely based on DMARC aggregate and forensic reports they receive from the recipient servers.
TLS encryption
This is yet another cryptography-based protocol that enables you to secure communications over a computer network. Its ultimate goal is to safeguard the integrity of the data transmitted between sender and receiver servers. In order to make sure that the email is encrypted while in transit, both the sender and receiver server must support TLS encryption.
HTTP proxy
Gmail Lag on macOS
Some users report that Gmail loads slowly on macOS, especially when background processes or security tools are consuming system resources. If macOS is slow, it may affect Gmail’s responsiveness. In such cases, optimizing system performance or using a lightweight browser may help improve loading times and overall email performance.
HTTP proxy serves as a middleman between the internet and your device. Suppose you are using Gmail through an email app or a web browser. In that case, the proxy handles the communication between your device and the Gmail server.
Here’s what it does:
Privacy
HTTP proxy hides the user’s IP address. This ensures that Gmail sees the proxy’s IP and not yours. Thus, your identity stays private and secure.
Security
The proxy also can block out harmful content or websites, thereby offering an extra layer of security while you are using Gmail.
Content filtering and monitoring
Organizations can use a proxy in order to control email access on Gmail by setting rules to monitor or block certain content.
Caching
The proxy stores frequently used content from Gmail (static files, images, etc.) so that it loads faster for the user next time.
CORS headers
CORS, or Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, is a mechanism that leverages HTTP headers to inform browsers which websites are allowed to access particular resources. This is significant for Gmail’s security while connecting to third-party services or using Gmail APIs.
Gmail’s API responses include security headers such as Access-Control-Allow-Origin. These responses define the domains allowed to access the resources. However, if the CORS settings aren’t configured the right way, it may lead to security risks. Threat actors can easily exploit this by using malicious websites to send out unauthorized requests on behalf of users, potentially compromising email security protocols.
Wrapping up!
Gmail has stringent security measures to safeguard your sensitive information, ensure privacy, and keep communications safe. As online threats become more advanced, it’s important for users to secure both incoming as well as outgoing messages.
If your business manages private emails, contacts, financial data, and significant pieces of documents, then Gmail’s security measures enable you to secure all the sensitive data and prevent any kind of data breaches.