Difference between phishing and spoofing
With the passing of time, cybersecurity threats are getting more sophisticated. That’s exactly why businesses and individuals must understand the nuances of cybercrimes closely. The two most common forms of cyberattacks are phishing and spoofing. In layman’s terms, people often overlap the two. However, each has a set of distinct characteristics and methods of operation.
This article breaks down the key differences between phishing and spoofing, thereby helping you inch closer to cyberawareness.
Phishing definition
Phishing is one of the most rampant cyberattacks where threat actors pretend to be legitimate organizations or individuals and dupe victims into sharing sensitive information. The data can include anything ranging from social security numbers, usernames, credit card numbers to passwords.
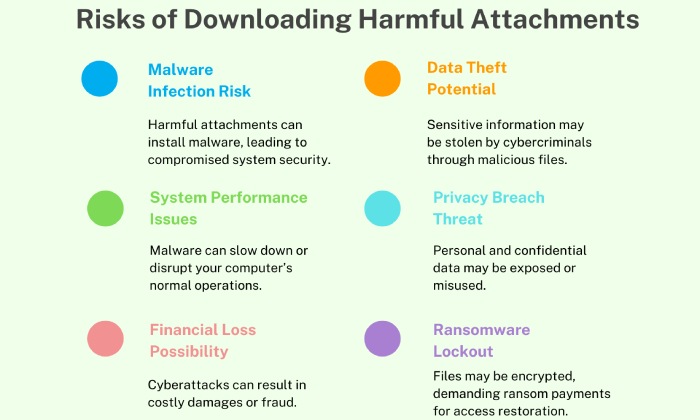
Threat actors execute phishing through SMS, emails, and social media platforms. The most prominent feature of a phishing attack is the sense of urgency, excitement or extreme fear in the content. The ultimate goal of the threat actor here is to trick the victims into clicking on a malicious link or even downloading a harmful attachment.
There are majorly 4 different types of phishing:
Whale phishing
This is a kind of social engineering attack primarily targeted on C-level executives with the motive to gain access to the victim’s PC, get access to their personal data and thereby make some quick money.
Spear phishing
This is a type of phishing attempt where threat actors target organizations or individuals with personalized communication. To carry out this attack, hackers send out malicious emails with the end goal of accessing sensitive data.
SMS phishing
SMS phishing, also known as smishing, is one of the most common cyberattacks where threat actors send out malicious text messages and trick the recipients into clicking on fake links or downloading harmful attachments.
Voice phishing
Voice phishing or vishing is when a threat actor tries to fool you and gain personal data through telephonic conversation.
Characteristics of phishing
Malicious links or attachments
Phishing emails generally contain harmful attachments or malicious links that are leveraged to access personal data or install malware.
Impersonation
Threat actors pretend to be reputed and prestigious entities (retailers, banks, government agencies), brands (Microsoft, Facebook), and individuals.
Emotional trigger
Phishing attempts aim at evoking emotions such as excitement, urgency, or fear in the minds of recipients. The idea is to compel them to take quick action without giving them much time to think and analyze.
Spoofing definition
Spoofing is a broader category of cyberattack in which the threat actors mimic any trusted source to gain your trust.
There are majorly 5 types of spoofing:
Email spoofing
Threat actors mimic the name and address of a known/reputed entity and use the same in the ‘form’ field of fake emails.
IP spoofing
Hackers skilfully alter the IP address while pretending to be someone else.
Caller ID spoofing
Threat actors alter their contact numbers with a number that the victim is familiar with.
Website/domain spoofing
An entire fake website or domain is created to mimic a known or popular entity.
GPS spoofing
Threat actors alter the GPS of a device to get it registered in another location.
Characteristics of spoofing
Identity theft
The main objective of spoofing is to pretend to be someone else, and that’s exactly why threat actors ‘alter’ everything, from email IDs, caller IDs, IP addresses, and GPS locations.
Technical manipulation
Threat actors rely heavily on technical manipulation to gain the trust of victims.
Automation
Unlike phishing, spoofing can take place in the background, even without the direct action of the victims.
Key differences between phishing and spoofing
Although both phishing and spoofing may seem related or interconnected on the surface level, there are some major differences between the two types of cyberattacks.
Purpose
The main goal of phishing is to get access to sensitive data such as financial information or personal details. On the other hand, spoofing is carried out with different motives, such as spreading malware, stealing personal data and redirecting web traffic to malicious websites.
Platform used
Phishing attacks take place through texts, emails, and social media messages. On the other hand, spoofing takes place through IP addresses, emails, phone numbers, GPS location, and so on.
Technique
Phishing is heavily reliant on social engineering techniques whereas spoofing involves technical manipulation in order to make a malicious conversation sound legitimate.
Action
Phishing victims are required to take action (clicking on a link, entering data or downloading an attachment). On the other hand, spoofing can take place on its own in the background.
5 sure fire ways to avoid phishing and spoofing
Phishing and spoofing cyberattacks are quite common nowadays. To steer clear of any kind of phishing or spoofing attack, here’s what you should do:
- Use 2-factor authentication.
- Ignore and delete suspicious emails and SMSes.
- Enable anti-spoofing features.
- Go for encrypted communications.
- Keep an eye out for any kind of suspicious activity.
The ever-evolving digital landscape requires you to stay well-versed with the latest cyberattacks and their nitty-gritty. Keep learning about the cyber world and prevent any kind of cyber scams or attacks.