These days, there’s so much talk about the classic technique of deception— phishing. Almost every day, you hear stories, read headlines, and even experience how cyber crooks deceive unassuming users into giving sensitive information, downloading a malicious file, or clicking on a fake link. These attackers usually make their way into your systems through fake emails pretending to be from your bank, text messages warning about “suspicious activity,” or phone calls from scammers claiming to be customer service representatives.
But would you believe us when we say that these cyberattackers were not always this savvy or proactive in their deception techniques? Or were they ahead of their time to pull off such devious tricks even in the early days of the internet?
Whatever might be the case, one thing is clear: phishing attacks have come a long way since they were first launched in the mid-1990s. What began as basic, mass-email fraud replete with misspellings and generic language has now evolved into sophisticated attacks that leverage advanced technology and social engineering to manipulate even the most vigilant users.
Let us take a look at how we have come so far (not for the good, though)!
Where did we get the name “phishing” from?
The word “phishing” is derived from the sport “fishing”. Just as a fisherman uses bait to hook fish, attackers exploit fake emails, websites, or messages to trick individuals into providing sensitive information. The moment the victim falls for the bait by clicking on an infected link, entering their login details, or downloading an infected file, the attacker can retrieve financial accounts, hijack identities, or download malware on their computer.
The “ph” in phishing comes from “phreaking,” an early kind of hacking that focused on breaking into telephone systems. John Draper and other hackers popularized the term after they discovered means of exploiting telecommunication networks. Cybercriminals later borrowed similar fake tactics for the internet, giving birth to today’s phishing attacks.
Since then, phishing has evolved into one of the most frequent and perilous cybersecurity attacks. So, it is very important that individuals and companies constantly have their guards up and are extremely vigilant when on the internet.
How did phishing start?
Phishing has been around for many years, but its origins date back to the 1990s when AOL (America Online) was among the largest online platforms. The hackers saw it as an opportunity, capitalized on it, and began to deceive AOL users by impersonating screen names to obtain their login credentials, passwords, and credit card data.
As the internet became more popular and accessible and emails became more prevalent, spammers changed their tactics. They no longer just employed false screen names, but they sent fake emails mimicking reputable companies. They would dupe individuals into clicking on forged links and giving personal details, similar to the phishing attacks we know today.
Phishing has evolved over the years to be more sophisticated and targeted. Today, we have various types, such as:
- Spear phishing – These are targeted attacks on individuals or organizations.
- Vishing – These scams happen over the phone, posing as customer service or tech support.
- Angler phishing – In angler phishing, the attackers spoof social media messages that trick users into divulging information.
- Whaling – These attacks on high-level executives or decision-makers are designed to steal sensitive company information or financial data or gain access to critical systems.
How did phishing attacks evolve?
Nowadays, the phishing attacks you are familiar with are far more advanced than they used to be. In the past, they were simpler to identify and avoid, but now, regardless of how proactive or alert you are, you can still become a victim of a well-designed phishing attack.
Let us see how the phishing attacks turned into the cybersecurity threat we see today:
The Love Bug of 2000
On May 4, 2000, people around the world received an email that said “ILOVEYOU” in the subject line. The message inside was simple: “Kindly check the attached LOVELETTER coming from me.” It seemed personal and harmless, so many people opened the attachment without thinking twice. But what they didn’t know was that this so-called “LOVELETTER” was actually a dangerous computer virus. As soon as someone opened the attachment, the virus started overwriting important files on their computer and spreading itself by emailing a copy to everyone in their Outlook contact list.
This virus, later called the “LoveBug”, was a game-changer in cybercrime. It showed how hackers could exploit both human curiosity and security weaknesses to spread malware quickly. The attack led to widespread chaos across the globe, infecting millions of machines. It was proof that phishing was not just a matter of password theft—it could also be used to seriously compromise entire systems.
Modern-day phishing attacks
The first attack of 2000 was an email-based scam, but today, these attacks have spread far beyond emails. They have made their way into text messages, phone calls, social media, etc.
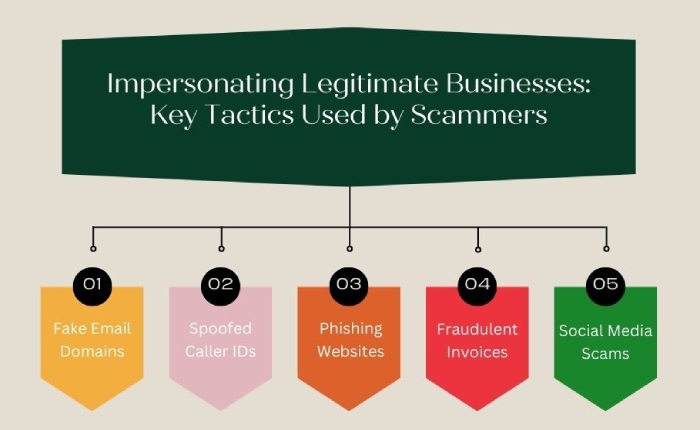
Attackers now impersonate legitimate businesses, government agencies, or even friends, with forged accounts and compelling texts to trick people into revealing personal information. These scams are no longer just simple emails with poor grammar—many phishing attempts nowadays are so sophisticated that even tech-savvy users fall prey to them.
That’s not all; they have also refined their ways to make their attacks more convincing and highly targeted. Instead of sending the same run-off-the-mill message to their targets, they now customize their attacks based on the victim’s personal information. This makes you believe that the message was meant for you and persuades you to engage with it.
Now you know that phishing attacks are everywhere, and the attackers try to stay one step ahead by constantly polishing their techniques. But that doesn’t mean you should fall behind! Up your cybersecurity game by deploying security protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC for your outgoing emails. These protocols not only authenticate your emails but also prevent cyberattackers from misusing your domain to carry out malicious phishing attacks.
Need help implementing DMARC for your domain? DuoCircle has you covered! Get in touch with us to book your demo today!