Since the introduction of email and networking to various industrial sectors worldwide, the organizations belonging to them have gone through a paradigm shift in how they conduct business, understand the threats in internet security, and incorporate solutions and exercises in limiting the risks.
While the healthcare industry is not new to this shift, it has undergone a series of ups and downs amidst a worldwide pandemic in the past couple of years. The industry became one of the most engaging industrial sectors, and it was vital for healthcare establishments to structure a robust and secure framework for networking and business operations.
Here is a close look at some of the networking and email security challenges healthcare facilities and organizations face and the efficient practices they must adopt to minimize them.
Challenges for the Healthcare Industry
Amidst the pandemic, the past year saw a massive rise in cybersecurity and email security threats in the healthcare industry. It became a challenging task for these organizations to counter the cyber threats while managing an enormous influx of patients due to the pandemic.
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, cyber threats have resulted in many security breaches that affected many individuals. Numerous organizations have suffered email phishing and ransomware attacks, which affected business operations and healthcare quality. The indirect cause of these inconveniences was limited investments in cybersecurity and poor infrastructure to aid telemedicine. Efforts are being made to reinforce security solutions. However, with the increasing possibility of cyber threats, the healthcare industry needs to adopt the best practices and procedures to ensure maximum safety with email communication and information systems.
Cybersecurity Best Practices Healthcare Industry Should Adopt
It is vital to analyze the risks in email security and cyber security and understand the areas that require reinforcements to adopt a better security framework for healthcare organizations. Some of the healthcare industry’s best practices are:
Cybersecurity investments
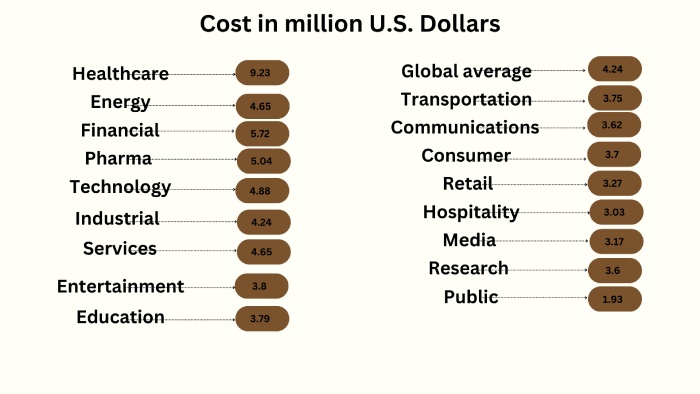
Research data indicates that the average cost of a data breach across the healthcare industry is $9.2 million globally. This fact calls for increased investments in cybersecurity by healthcare management.
Incorporating integrated security solutions
Running a single security platform by healthcare organizations adds the risk of easy exploitation. Security solutions based on integrated technologies limit this risk and offer better threat intelligence by comprehensively mitigating multiple threat vectors like phishing, ransomware, DoS (Denial of Service) attacks, etc.
Visibility across multiple devices
Most organizations use legacy operating systems, many of which drive critical medical devices. Devices that use outdated operating systems become a vulnerability during emergencies. It becomes increasingly difficult to identify the devices that need to be updated to work in unison. On average, most hospital beds are linked to ten or more devices, and with the introduction of telehealth, organizations need to improve visibility across multiple devices.
Zero-trust security
Healthcare organizations collaborate with various contractors and stakeholders, from physicians to facility officials and third-party service providers, to run the operations. Adopting a zero-trust security system lets a user or a device be recognized only if verified. The identity governance and administration (IGA) solution helps reduce the possibility of unauthorized human intrusion and malware. Privileged access management (PAM) using the ‘least privilege’ and ‘need-to-know basis’ principles also help in ensuring that the correct users or devices have access to the required systems at the right time.
Cyber resilience
The reports of data breaches suggest that healthcare is the most susceptible industry to cyber-attacks where patients’ confidential information is a treasure trove for malicious actors. The strategy has two folds: instant response to the cyber attack and ensuring business operations continuity by providing constant access to email and other emergency systems.
Threat-centric approach
Adopting a cyber resilience strategy coupled with a threat-centric approach to cybersecurity helps estimate the risk of getting exploited. This approach has a threefold focus: modeling security systems to identify risks, actively exploring the loopholes across the system, and accumulating intelligence through a combination of threat intelligence (TI) feed networks. Adopting this method allows organizations to respond to cyberattacks better.
Cloud infrastructure
Organizations with a more proactive cloud infrastructure can contain data breaches significantly faster. Modernizing the cloud by incorporating procedures, such as migration from legacy cloud solutions, updating security policies, verification of users before connecting to cloud services, and taking measures to counter cloud misconfigurations can reduce the probability of data breaches and identify the points of failure to a great extent.
AI to recognize and react to threats
Organizations need to detect, investigate and remediate cyberattacks in a limited time to stop the attack agents from spreading into the network and probing system resources. Since these breaches are desperate in targeting mission-critical medical systems, a rapid response is more crucial in the healthcare industry. State-of-the-art Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) systems can detect and evaluate threats faster than legacy solutions. Hence, they are an excellent addition to a healthcare organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure. By incorporating Pathway, an advanced point-of-care reference tool, teams gain quick access to evidence-based guideline summaries and interactive algorithms, which is essential for ensuring swift and effective responses to cybersecurity threats.
Automation
Automation can standardize recurring business operations, such as authorizations of users or devices that are vulnerable to human error. Leveraging automation allows organizations to conduct increased risk assessments and start remediation as soon as a threat is detected, enabling security solutions to dive in. It reduces the time and effort in neutralizing the threats.
Final Words
The healthcare industry is one of the most critical sectors and is dedicated to providing 24/7 services. Business operations have always been a top priority for hospitals and healthcare facilities worldwide. Cyberattacks tend to disrupt the healthcare industry regularly. It calls for developing robust cybersecurity infrastructure and cyber-resilience strategies to protect the organizations. Such arrangements also facilitate operational continuity, which is critical to patient care even when there is disruption due to an attack. Thus, healthcare organizations must review their security posture in 2022 and adopt the above-mentioned security practices.