The risk of personal data getting misused has become more and more at risk with each passing day. Health reports can be divulged, financial details can be stolen, and contact information can be taken advantage of by marketers. These are just some of the ways people’s online information can be jeopardized.
If your business is holding the stakeholders’ and clients’ information online, you’ll have heavy accountability for data leaks like phishing. To ensure safety and keep your business’ credibility in check, data anonymization is one of the best measures you can put in place.
In this post, we’ll consider what data anonymization is and why it’s important. We’ll also go over its pros and cons. Foremost, we’ll talk about the techniques you can practice to anonymize data for your business and your client’s safety.
Let’s start by understanding what data anonymization is.
Data Anonymization In a Nutshell
Data anonymization is the exercise of protecting sensitive and private information by encrypting or deleting identifiers that link a stored data set to a specific person. It’s a technique used by organizations to abide by data privacy regulations requiring the security of PII or personally identified information like financial details, content information, and health reports. For many enterprises, implementing anonymization effectively requires a broader governance framework, often guided by structured data strategy consulting services to align privacy controls with regulatory and operational objectives.
For example, a financial institution can encrypt the name, biometric data, and other identification details of users when doing financial transactions like making deposits in a bank. It prevents any attacker from tracing the person, stealing their details, and assets.
The data that can be included in the anonymization are, but are not limited to:
- Names
- Contact numbers
- Addresses
- Social security numbers
- Photographic images
- Date of birth
Data anonymization protects private information and activities while preserving the collected data’s credibility. The General Data Protection Regulation or GDPR outlines rules specified to protect user data. While it allows the collecting of anonymized data without consent, it outlines that all identifiers should be altered or removed and this is where data anonymization comes in.
Simply said, data anonymization obscures the personal data collected by organizations so they can use it for any legal purpose they have without jeopardizing the identity and personal information of the individuals involved. Emails can be collected for abandoned cart sequences and can be freely done as long as sensitive information and details are not divulged.
However, one important thing to note is when a data set passes through several sources, de-anonymization techniques can be applied by attackers to retrace the data anonymization procedure to reveal personal information they can take advantage of.
Still, practicing the data anonymization procedure is vital. Masking sensitive attributes as part of an organization’s data safety measures gives a higher level of security for its stakeholders and all other people involved.
At a glance: data anonymization removes confidential information from raw data that can be associated with a specific individual, project, or organization. It protects identities, other sensitive information, and private activities.
If you’re a business that requires collecting sensitive information, what data collected should be anonymized? Let’s consider that next.
Sensitive Data That Should Be Anonymized
Granted, not all data collected should be anonymized like in contact forms that are consciously filled up. Hence, the database administrator needs to identify which is sensitive and should be obscured and which ones aren’t. The answers may differ in different industries and sectors, but while some information is subjective, some should be anonymized.
But here are the basic types of information that should be anonymized whatever industry it’s under.
I. Name
The name is arguably the most common identifier of a user in a data set. With this information, attackers can easily trace the data source and other pertinent information. So this should be properly obscured.
II. Mobile Number
If in the past, pesky marketers are the only people you worry about when your mobile number is divulged, today, there’s more to be concerned about. You see, your mobile number is like a gateway for other information related to you to be revealed.
Worse, they can use your number, even duplicate it so that security measures like OTPs get redirected to them instead of to you thus stealing other precious information and even the money you have in the bank.
That’s just the tip of the iceberg, attackers can do a lot more when they hold your mobile number so it must get anonymized.
III. Photograph
Other than your name, your photo is the other element that quickly ties you to a data set. During an identity verification, often, photos of you are collated. Hence, data anonymization allows this vital detail of you to be obscured to keep you and the rest of your data safe.
IV. Credit Card Details
If you’re running a website that manages financial transactions and payments like the eCommerce store selling Valentine’s Day lingerie or Impossible, one that’s selling sports essentials, likely, you’ll be gathering credit card information of your clients. It can include the credit card number, the pin, and even the code at the back of the card. Put no anonymization in place, this sensitive information will get into the hands of attackers easier costing you the trust of clients and others who’ll know about this breach.
V. Passwords
Some backend systems save passwords. Without encrypting them, an attacker can conveniently impersonate a client or someone in your organization to steal more information and money from the bank. People are always reminded to keep their passwords a secret even to family and friends hence your organization should do an extra measure to keep this sensitive information safe from attackers.
VI. Security Questions
Security questions are used to identify and verify a user as the owner of an account, hence if an attacker gets a hold of this, he can gain full control of the account, steal information and even steal the identity altogether. Strongly consider encrypting this information too.
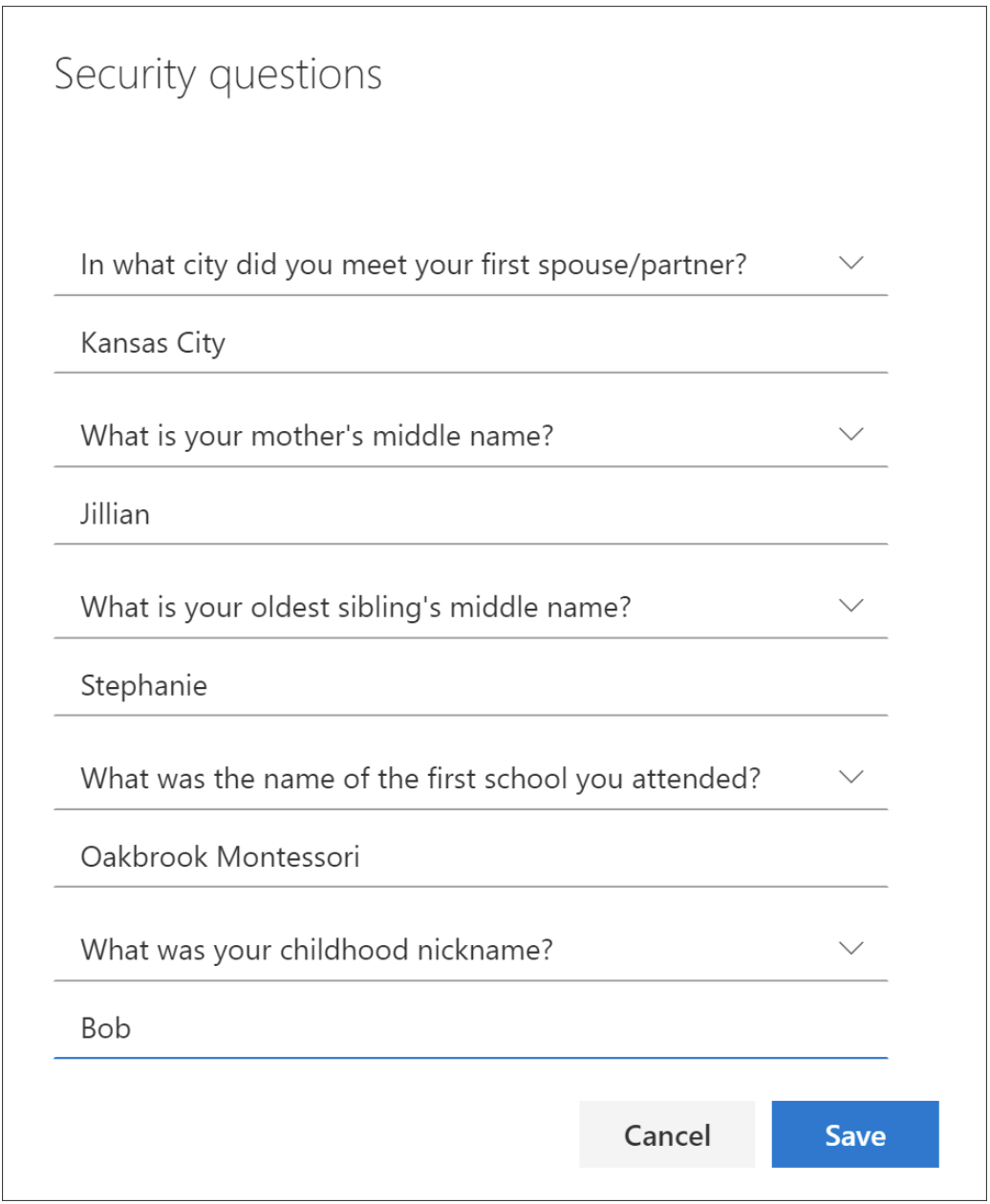
Source: microsoft.com
The list can go on depending on the organization involved. At the end of the day, it’s the database administrator’s responsibility to review company policy and privacy laws to figure out which information would pass as sensitive and which doesn’t. When identified, prompt data anonymization should follow.
So now that you’ve identified which information should be obscured, how can you do it? We’ll consider that next in the data anonymization techniques.
13 Data Anonymization Techniques You Can Try
With data anonymization, there are multiple means that lead to the same end. There is a bit of difference in the data forms and technicalities but the underlying principle is generally the same.
1. Data Masking
Data masking involves concealing data by using altered values. In this technique, you hide information by modifying or mirroring the original values with inauthentic ones. You can do this by encryption, character shuffling, or character substitution.
As an example, if the original character is “R” you replace it with “L”. Replacing the values this way can make reverse engineering much more difficult for attackers wanting to take advantage of the information you collected.
Data masking comes in four different types, let’s consider each one briefly.
- Dynamic Data Masking: with this type, a single data set is substituted by smaller sets and moving it from its current system to another.
- Deterministic Data Masking: this type involves putting the same values into two data sets. One is an original data set and the second is the improvised data set.
- Static Data Masking: this type is a process of altering every sensitive dataset in a database. Thereafter, this data is transferred to a new location and the original dataset is kept as a backup.
- On The Fly Masking: This type is comparable to dynamic data masking, the difference lies in the destination. With this type, the subsets are moved to a new dev./test environment within a secondary storage system.
2. Pseudonymization
With pseudonymization, data is de-identified by substituting private identifiers with fakes ones, or as the name suggests, pseudonyms. For instance, “Mary Gartner” is replaced with a “Stella Scott” identifier.
Pseudonymization preserves data integrity, accuracy, and statistical precision while at the same time keeping it confidential. This way, the data can still be effectively used for training like what Axonify offers, testing, analytics, development, creation, demo operations, and development while maintaining data privacy.
Additionally, this technique makes cross-referencing with sources and decoding easier when compared to other data anonymization methods.
3. Generalization
Generalization involves deliberately excluding some parts of the data to make it less identifiable. In this technique, the data will be modified into a set of ranges or large regions within appropriate boundaries.
For instance, when generalizing an address, the house and block number can be removed but the street name is retained. Specific data is removed but a measure of data accuracy is maintained. This exemplifies the fundamental principle of data anonymization.
4. Data Swapping
This technique is also known as shuffling or permutation. What it does is reorganize the dataset’s values so it doesn’t suit the original records. This includes attributes like date-of-birth and others that have a major impact on anonymization. This method also makes it hard for attackers to de-anonymize because of the mismatch it comes with.
5. Data Perturbation
Data perturbation is applicable on anonymizing data sets that cover numerical inputs repricing details. It modified the data sets a bit by applying round-numbering techniques and adding some random noise.
However, with this technique, the values must be proportional to the perturbation. Utilize a small base and the data sets utility will be reduced. For instance, it’s best to use a base of 5 for rounding values like a house number or an age since it’ll be proportional to the original value of the attribute.
6. Synthetic Data
Synthetic data is a data anonymization technique that involves algorithmically manufactured information that has no relation to real events. Mathematical models are constructed based on the patterns of the original data set. Statistical methods like linear regression, standard deviation, and median among others are used to come up with synthetic prototypes.
Some database administrators view this method as a fancier way to anonymize data rather than make alterations right on the original data sets.
These six methods are the most commonly used data anonymization techniques, however, seven more can be tested out.
7. Aggregation
In this method, data is collected in its entirety and summarized. As an example, addresses are excluded in the data set, but the number of people living in that location is known. This is usually used when the information is put up for sale.
8. Custom Anonymization
Custom anonymization is implemented by using a mixture of techniques that uses applications or scripts.
9. Directory Replacement
In this technique, changes are made to the data but keep consistent relations with other values. It partly involves pseudonymization but to anonymize, information that is separated but identifies the information is deleted.
10. Encryption
In this method, instead of removing sensitive data, it’s encrypted to make it unreadable unless a decryption key is provided. This will be helpful for financially sensitive documents like invoice generators.
11. Hashing
Simple, data points are substituted with a hash, and an example of this would be an alphanumeric string.
12. Randomization
In randomization, much like data perturbation, noise additions are used to make sensitive data imprecise.
13. Nulling Out
In this method, sensitive data is completely removed making those attributes null values.
Learning about each technique can be overwhelming, but just to simplify things, here are a few best practices you work on in every data anonymization you do.
Data Anonymization Best Practices
The best practices begin with designating a team or an individual to manage and evaluate forms, processes, and documentation. The person responsible should then:
- Comprehend why the request was made
- Evaluate the issues and risks
- Analyze and identify the attribute that needs to be anonymized
- Gather the needed information in connection to the resources available
- Ensure that projects are approved and completed accordingly
But is data anonymization really good for your business? Here are some advantages to convince you.
The Benefits Of Data Anonymization
A. It Protects Against Misuses and Exploitation Risks Of Insiders
Sometimes people who have access to the data can be tempted to exploit, misuse, or share the data in exchange for some personal benefit. To be dissuaded to take part in any data perversion, employees should themselves have limited visibility even with the access that they are given.
B. Protects Against Loss Of Trust And Market Share
A factor in an organization’s credibility is the ability to safeguard personal and sensitive information. Have the reputation for being unreliable about sensitive information and no person or institution will even be willing to do business with you thus also reducing or losing market share altogether.
Practicing data anonymization ensures stakeholders that the company puts a high value on its responsibility of securing sensitive and confidential information through complex and multi-layered data protection measures.
C. Heightens Supervision Control And Consistency Of Results
Having data anonymization in place increases governance allowing your organization to leverage apps and services including big data analytics. It also promotes consistency of results, fueling digital utilization ensuring users that data protection is applied to this increasing new market value.
D. It Serves As A Damage Control Measure
Why wait for a disaster to happen before you put measures in place. With data anonymization techniques applied, you’ll be curtailing data loss and data breach helping you avoid the repercussion if ever anything untoward happens.
E. Peace Of Mind
Having this safety measure in place gives you reduced fear, even peace of mind that you can carry out operations and transactions without any risk in between to make your employees a high-performing team.
While there are significant benefits, there are also disadvantages to data anonymization. Check out what they are so you can fully comprehend if this is a route you should consider for your database.
Drawbacks Of Data Anonymization
While data anonymization provides safety, it can adversely affect some of the goals you have for collecting data in the first place. Gathering obscure data and removing certain attributes will restrict your capacity to extract meaningful insight from the data collected.
With the data becoming less coherent, database administrators and analysts will take longer to make valuable improvements to projects.
Think about audience targeting for improving user experience in content like High Desert Pure hemp lotion blog or, anonymizing data will limit valuable insight needed to make meaningful adjustments to the current layout, dynamic, and structure.
Add to that is the fact that with varying techniques that can be applied is the difference in the efficacy of each. Unless you thoroughly understand what techniques work best for a certain endeavor, you can end up losing valuable information hindering you from making the most meaningful improvements.
Conclusion
If safety is the main concern for data gathering, data anonymization is a no-brainer measure to apply. It makes for safe transactions thus increasing credibility, and market share in the long run.
However, if the quality of data is more important, it comes with some drawbacks. The good thing is, as long as you know what kind of data you need and you understand how the technique works, you can practice a method that is both safe and preserves the quality of the data you need.
Overall, with the rampant risks in cybersecurity, putting together layers of security doesn’t just benefit the organization but also its users. What you gain by doing this technique far outweighs any data quality loss.