In the ever-evolving digital landscape, cyber threats are constantly mutating and growing in sophistication. As we turn the digital pages of another week, we’re met with a slew of cyberattacks that have stirred conversations and raised eyebrows across the tech sphere. Here’s a close look at the latest email security news causing debates in the tech industry.
Google and Yahoo Introduce Enhanced Email Authentication Standards for 2024
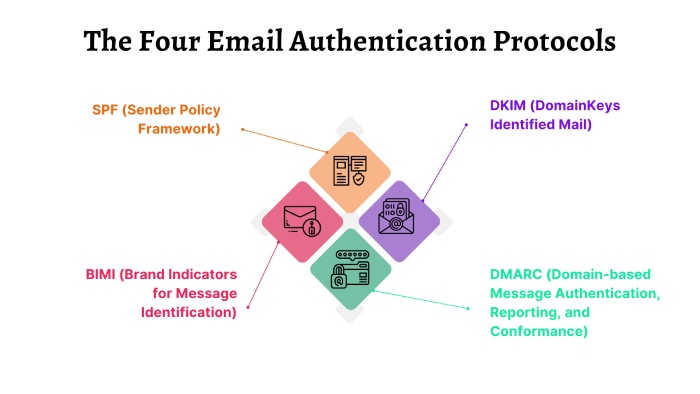
Google and Yahoo have unveiled stringent email security requirements set to be enforced from 2024. Starting early next year, mass email senders on Gmail and Yahoo Mail must adhere to robust authentication protocols, encompassing DMARC, SPF, and DKIM, as part of established best practices.
This initiative aims to enhance the detection and blocking of malicious messages, ensuring cleaner inboxes for users while curbing attackers’ ability to exploit resources undetected. As per Gmail and Yahoo guidelines, these bulk senders must also facilitate easy unsubscription and confirm they are only sending desired emails. The absence of secure email authentication protocols exposes organizations and users to increased risks of Business Email Compromise (BEC) and phishing attacks.
Commencing Q1 2024, Gmail and Yahoo Mail will mandate bulk senders to implement the rigorous authentication measures for email security, closing potential avenues exploited by attackers.
Neil Kumaran, Group Product Manager for Gmail Security and Trust, expressed the shared industry goal for a more secure email ecosystem, emphasizing collaboration to elevate global email standards. Marcel Becker, Senior Director of Product at Yahoo, echoed this sentiment, highlighting the collective effort required to establish these impactful changes as the new industry norm for email protection.
New BMC Vulnerabilities in IPMI Firmware Raise Concerns for Supermicro Servers
Prominent server and computer hardware manufacturer Supermicro has released crucial updates to rectify numerous security vulnerabilities in their Baseboard Management Controllers (BMC) IPMI firmware.
These vulnerabilities, categorized as CVE-2023-40284 to CVE-2023-40290, were identified by the security enterprise, Binarly. They could allow remote attackers to gain root access to the BMC system if exploited. Of particular concern are three cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in the BMC server front-end (CVE-2023-40284, CVE-2023-40287, and CVE-2023-40288). These could be exploited remotely without authentication, allowing the execution of arbitrary JavaScript code.
According to Supermicro, these security vulnerabilities hold a CVSS score of 8.3. Binarly, however, rates them as under ‘critical severity’ with a score of 9.6, assuming that the attacker possesses knowledge of the BMC web server’s IP address and the administrator’s email.
Supermicro has acted promptly and has reported that there were no instances of malicious exploitation of these vulnerabilities. Binarly’s research, focused on the web server component, has revealed over 70,000 cases of internet-exposed Supermicro IPMI web interfaces, underscoring the critical need for prompt patching of vulnerabilities and strengthening cybersecurity measures.
Severe Exim Mail Transfer Agent Flaws Could Result in Data Exposure and Remote Code Execution
A severe zero-day vulnerability has been detected in all Exim Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) software versions, allowing unauthenticated attackers to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE) on exposed servers.
Discovered by an anonymous researcher and revealed through Zero Day Initiative (ZDI), the flaw (CVE-2023-42115) arises from an ‘Out-of-bounds Write’ weakness within the SMTP service. This vulnerability in the default TCP port 25 SMTP service results from insufficient validation of user-supplied data, enabling attackers to execute code within the service account’s context.
Despite ZDI reporting the issue to the Exim team in June 2022 and resending information at the vendor’s request in May 2023, developers have yet to provide an update on their patch progress. ZDI released an advisory on September 27 detailing the CVE-2023-42115 zero-day and the complete exchange timeline with the Exim team.
Exim developer Heiko Schlittermann revealed that fixes are available for some vulnerabilities, but others require additional information. ZDI intends to update its advisories once Exim publicly releases patches, emphasizing the critical need for swift action to secure vulnerable systems.
Elaborate Phishing Attack Hits ‘Indeed’ Job Listings, Resulting in Microsoft 365 Account Lockouts
A recently exposed phishing operation has been targeting high-ranking executives within U.S. organizations, exploiting open redirects from ‘Indeed,’ the job listings site.
The attackers employ the EvilProxy email phishing service, capable of harvesting session cookies, enabling them to bypass multi-factor authentication protocols. Menlo Security researchers uncovered this campaign targeting executives from diverse sectors, including electronic manufacturing, finance, real estate, insurance, and property management.
The threat actors manipulated open redirects, essentially URLs that automatically direct users to different online destinations, to lead users to a deceptive Microsoft login page. Upon accessing the seemingly genuine link, victims were redirected to a phishing site operating as a reverse proxy for Microsoft’s login portal.
Notably, this incident follows a previous EvilProxy campaign flagged by Proofpoint in August 2023, pointing to the escalating use of reverse proxy kits in email phishing. With the integration of open redirects, the efficacy of these malicious attempts is enhanced.