Understanding Global Data Compliance Laws in 2023
The responsibility of handling data comes with its own intricacies, but adhering to global data compliance laws makes the situation a bit sorted. By sorted, we don’t mean easy, but rather uniform. These laws are introduced to safeguard the privacy of customers and users while ensuring companies run their operations using the requisite details and documents. Moreover, adhering to these laws and best practices reflects your concern about cybersecurity, which consequently boosts your image as a responsible and trusted company.
We have gathered this guide on global data compliance laws to help you safely expand your clientele across borders while cohering to legislation. Discover how these regulations ensure responsible data handling and safeguard customer privacy.
We explore key laws, including GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, and discuss their implications. Learn about the complexities of data compliance, such as varying penalties and jurisdiction issues, which businesses need to navigate when expanding. Stay informed with our concise guide on this critical topic.
What is Data Compliance and Why is it Important?
Data compliance is the process of considering legislation and governance to oversee data privacy. In simpler words, it instructs you on how to handle the data within your organization. This involves handling and administrating information tied to consumer privacy, data security, and data storage requirements. It also includes applying measures for phishing protection and addressing cyber attacks in order to prevent and alleviate their impact.
Consumer data is beyond just contact details, and humans are linked with every piece of information companies store in their databases. Thus, it’s vital to ensure malicious actors don’t get their hands on it.
There is no doubt that businesses run on a database, and it is extremely valuable for operations, strategizing, and scalability through enhanced user experience. Thus, data security laws across the world are constituted to protect the privacy of everyday people as well as the security of a brand’s digital data assets.
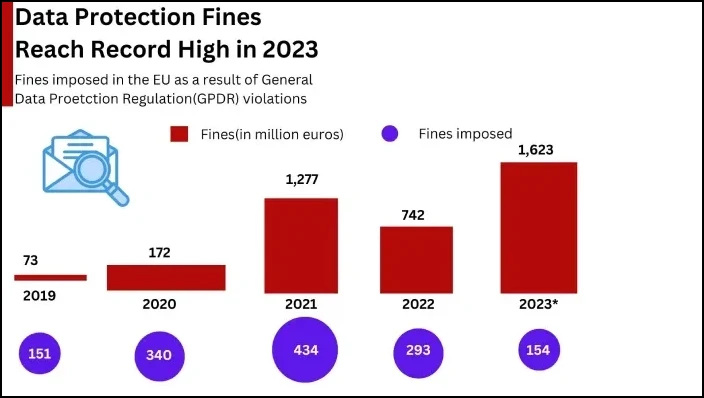
GDPR, short for General Data Protection Regulation, is regarded as the toughest privacy and data security law worldwide that was initially drafted and passed by the European Union. It obligates companies anywhere in the world if they target or collect data of EU citizens. Despite the fact that GDPR has established itself as a statutory, but a substantial ratio of organizations are still unsure of the specific data legislation meant for them.
The parties involved and affected by data compliance legislation are data subjects, data controllers, and data processors.
Data subjects are individuals whose personal information is stored, retrieved, retained, traded, or handled by an organization. If you send emails, your data subjects encompass your recipients, which includes anyone whose email address you maintain in your records.
Data controllers evaluate the purpose and means by which sensitive data is processed. Lastly, data processors carry out the actual processing of the data.
Consumer Privacy Laws
Here are the three data guiding rules that are implicated for businesses based out of the US:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR marks a groundbreaking shift in data rights protection by tuning in transparency and individual data control. It enforces substantial penalties for breaches and operates on the principle that individuals entrust their data to service providers rather than giving it away at sign-up. Its primary aim is to provide the highest level of protection to consumers.
Important points to keep in mind:
- Enforced starting from May 25, 2018.
- It standardizes data protection regulations across the European Union.
- It applies to any business that handles data of EU citizens, regardless of their location.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act shields the rights of individuals based out of California. GDPR-compliant organizations don’t require significant efforts in adhering to the CCPA law. It empowers consumers with rights to access, delete, and opt out of the sales of their information. They are also allowed to demand to understand what data businesses collect and how it’s used.
It mandates businesses meeting certain criteria to be transparent about their data practices and imposes penalties for non-compliance. The compliance law imposes a strong precedent for data privacy laws worldwide. This underlines the necessity of individual data protection and the requirement for businesses to respect their customers’ privacy rights.
Important points to keep in mind:
- Enforced starting from Jan 1, 2020.
- It standardizes data protection regulations across California state.
- CCPA applies to any business that handles data of Californian residents citizens.
Businesses subject to the CCPA must provide clear and accessible opt-out guides to enable consumers to easily exercise their right to opt out of the sale of their personal information.
This underlines the necessity of individual data protection and the requirement for businesses to respect their customers’ privacy rights.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act is an important piece of healthcare legislation in the United States. Enacted in 1996, HIPAA serves as a safeguard for the privacy and security of individual’s health information. Its primary objectives are to ensure the portability of health insurance coverage for employees, even when changing jobs, and to establish stringent standards for the protection of sensitive patient data.
HIPAA places strict requirements on healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearing houses to maintain the confidentiality of patient records and regulate the transfer of medical information. It also empowers patients by granting them certain rights to access and control their health information. HIPAA plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of healthcare data, promoting trust between patients and healthcare providers, and upholding the privacy and security of sensitive medical information.
Compliance Laws’ Limitations
Not all legislations are created equally, and this creates an issue for businesses trying to expand to other states and countries. Here’s what you need to bear in mind-
Data Jurisdiction
It doesn’t matter where your company is based out of; what matters is the location of the data subjects.
Data Impact
Small-scale organizations need not be represented in legislation.
Penalties
The fines for violations lack uniformity, as they vary between different authorities. Some impose penalties based on a percentage of the company’s net turnover, whereas others assess fines on a per-affected subject basis for each breach.
Final Words
Prioritizing data compliance comes with some challenges and limitations. It’s suggested to keep yourself informed of the updates or outsource the responsibility to a specialized team.