The digitized age has witnessed malicious actors and cyber adversaries singling out MSPs as their key targets. Be it ransomware, data breaches, phishing attacks, or any other mode of attack, MSPs remain at the frontline against attacks. By targeting MSPs, attackers can find easy victims in their clients, who often appear to be sitting ducks for malicious actors. Amidst these challenges, top MSPs are reinforcing their defense line to secure themselves and their clients.
Presently, attackers go beyond encrypting the systems of MSPs. They deploy compromised employee credentials of the MSPs for hijacking their tools. Ultimately, they utilize these tools for triggering ransomware attacks on their clients. Given that traditional defense systems against adversaries are obsolete, MSSPs need to develop fresh strategies to secure themselves.
Statistics That Prove The Importance Of Adopting Cybersecurity Measures For Organizations (and MSPs)
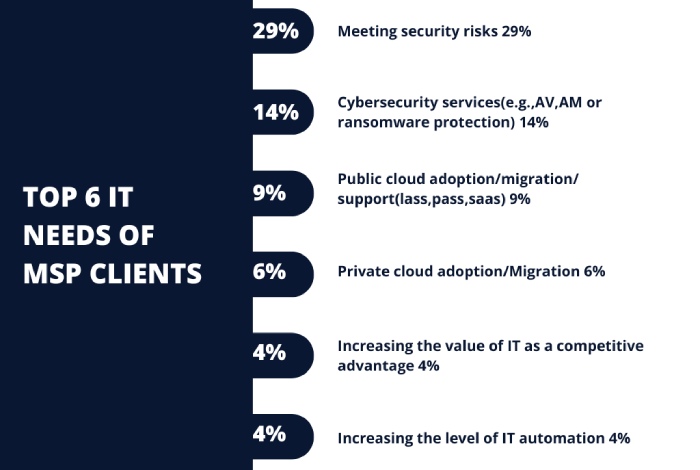
The below graph shows the IT requirements of clients for which they rely on MSPs and MSSPs. In other words, these IT segments of clients and the critical data and digital assets associated with them are at the risk of cyberattacks if the MSPs are not secure enough. MSPs can realize the severity of the situation by looking at the additional statistical data listed below.
- Cybersecurity continues to be one of the essential components of managed service providers. 77% of the MSPs believe that 10% to 20% of their clients suffer at least one online attack every year.
- The emerging threat landscape in the virtual space is evident from the fact that more than 44% of the clients of MSPs depend on three or more email security solutions. It tells the story of the kind of vigilance required to be in place to draw the line of defense.
- 37% of the players believe MSPs were more susceptible to cyberattacks in 2020 than in 2019.
- The leading MSPs are enjoying higher revenues from their clients, as the latter are increasingly turning to them for more robust security measures. Almost 95% of the MSSPs witness their clients reaching out to them for counseling on the best cybersecurity practices.
- Forward-thinking MSPs are capitalizing on the business opportunities arising from cyber threats. Around 73% of the MSPs experienced their revenues growing over the last year. These service providers have expanded their portfolio of services, offering antimalware, firewall, antivirus, OS patching, and VPN management services.
- More than 33% of MSP clients reported multiple attacks over the internet on the same day. The fact points to the importance of adequate cyber defense for managed service providers.
- Small businesses account for as much as 43% of cyberattacks. It explains why most SMBs are reaching out to managed service providers to strengthen their cybersecurity posture.
- 90% of the SMBs count on managed service providers for the right kind of defense mechanism.
- In the last two years, as much as 79% of MSPs reported that their clients had experienced ransomware attacks. It points to the importance of adopting the right anti-ransomware solutions to keep the organization’s information assets from falling into the hands of cyber adversaries.
From the above points, weighing the vulnerabilities against adversaries makes sense for MSPs and MSSPs to invest in appropriate security mechanisms.
What Makes MSPs A Prime Target For Adversaries?
Over the last couple of years, malicious actors have taken advantage of the “work from home” scenario. They have left no stone unturned in targeting employees worldwide, especially MSPs, as these are essentially a goldmine of data. On the other hand, organizations and enterprises are also turning to the reputed MSSPs for better security, making them even more lucrative from the threat actor’s perspective. Here are some common reasons that make MSPs a key target for cyber adversaries.
Taking Down Several Organizations At Once
The malicious actors can benefit substantially from attacking managed service providers considering the relatively less effort involved. The attackers find it easier to compromise a single victim while it can access the credentials of their clients. Rather than attacking each client of the MSP, the malicious players try to take the MSP down. Once they hold an MSP hostage, all their clients would automatically come under their control. Each impacted client needs to pay a small ransom during ransomware attacks while the MSP struggles to find a quick solution.
Gaining Access Through RMM Tools
Presently, MSPs largely depend on RMM (Remote Monitoring Management) tools for accessing the environments of their customers. It enables them to execute the respective tasks for which they are responsible. The threat actors can obtain the credentials to these tools using social engineering and deploy the same set of tools for malicious purposes and remote access in a compromised situation. Besides, They habitually exploit them through unpatched vulnerabilities. Malicious actors also use malware or brute force for capturing credentials or execute attacks for guessing passwords.
Obtaining Administrator Credentials
Once an MSP’s security system gets compromised, the threat actors can quickly obtain the administrator credentials. In the process, they can access the RMM tools for injecting malware into their customer’s systems. Thus, the malicious players can exploit the MSP’s clients without attacking them directly. Once the security mechanism falls back, it opens the doorway for information theft straight from their clients as well. Therefore, malicious actors target MSPs these days rather than individual clients.
Fundamental Cybersecurity Measures MSPs Must Adopt To Keep Their Information Assets Safe
Leading MSPs prefer staying abreast with the latest security protocols to leverage their line of defense against malicious players. Here are specific recommendations for MSPs that can help them secure their systems and that of clients.
Restricted Access To Network
A significant section of the recent attacks has landed on the MSPs’ networks and expanded thereon. To mitigate the risk, one must establish barriers between their assets and the users. MSPs need to list down all the network assets as the first step. Next, classify them as per the risk level and monitor access to the same.
Make Passwords Unique And Strong
As an MSP administrator, one would be aware of the value of passwords. Use MFA wherever possible, and make passwords case-sensitive using numbers, letters, and special characters. Do not reuse the passwords or share a single password with a different account. You may also deploy a robust tool for password management, which can significantly help mitigate data breaches. Here are a few additional tips related to password security.
- Never store password credentials in the browsers. Malicious actors can easily scrape caches in browsers using malware.
- Try out trusted Password Management Solutions such as the LAPS (Local Administrator Password Solution) of Microsoft.
- Change all default usernames, such as ‘user,’ ‘root,’ ‘admin,’ etc., in the first possible instance.
Arrange System Auditing For Inactive User Accounts
Many user accounts continue to remain inactive though they appear to be enabled (for instance, if an employee has left the organization). These access points open up gateways for cybersecurity breaches. With regular audits implemented through a clear policy, one can delete and disable user’s accounts once they leave the organization.
Block Lateral Movement Among Workstations
Most of the recent attacks go beyond a single workstation. Malicious actors design the attacks to affect a particular point in the system and expand from there. MSPs need to deploy Firewalls, Robust Group Policies, and Active Directories to prevent communication between different workstations. It can help isolate an affected system while the remaining ones stay secure.
Secure Remote Management Tools
With many organizations having employees operating from home, MSPs are increasingly using remote management tools. While these tools can help scale up a business, they can also attract attackers. By attacking these tools, a malicious player can get direct access to the customers’ credentials.
Here are some guidelines that would help you secure the remote management tools.
- Make sure to restrict access to the software used for remote management.
- MSPs should limit the availability of remote access tools to their staff based on their roles.
- Deploy strong and unique passwords with MFA in remote access tools.
- Limit the access of remote accounts only to required resources.
- Update the remote management software regularly.
- Do not use domain administrator accounts for logging into the workstations as malicious actors harvesting credentials would make their way into the system.
- Address the vulnerabilities and apply security patches regularly as attackers can exploit loopholes for unauthorized access.
- Enable centralized monitoring and logging for alerts associated with remote access sessions.
- Capture relevant information on remote access activities and sessions that would enable one to carry out audits, investigate suspicious activity, and spot anomalies.
Secure Remote Desktops
For MSPs, securing RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) can be an essential security element. However, when one fails to do so, it can lead to major data breaches. Unless necessary, do not expose the RDP or any of the internal resources to cyberspace. If there is an alternative way to carry out what is required, it is prudent to follow it. One might deploy port scanners to identify remote desktops that are exposed to cyberspace. Some of the scanning tools like Shodan or Nmap can prove beneficial. Since malicious actors would be already prying on the systems, one must check out how the network appears to them.
Final Words
The range of services offered by MSPs to their clients is broad. It implies that any security issue with an MSP’s network will reflect very poorly on the critical information assets the clients have entrusted to it. And, malicious actors of today are highly sophisticated, well-structured, and systematic in their moves. Being an MSP, one needs to acknowledge that they may already be a target for malicious actors. Hence, they must also educate the clients on the best practices as part of the security policy.
The secret to secure oneself lies in hiring dedicated staff who are ready to learn. In the process, one can also bridge technical loopholes present in tools. With proper training, cultivating cyber-resilient behavior, and using robust email security solutions, MSPs can ward off the strongest of adversaries.