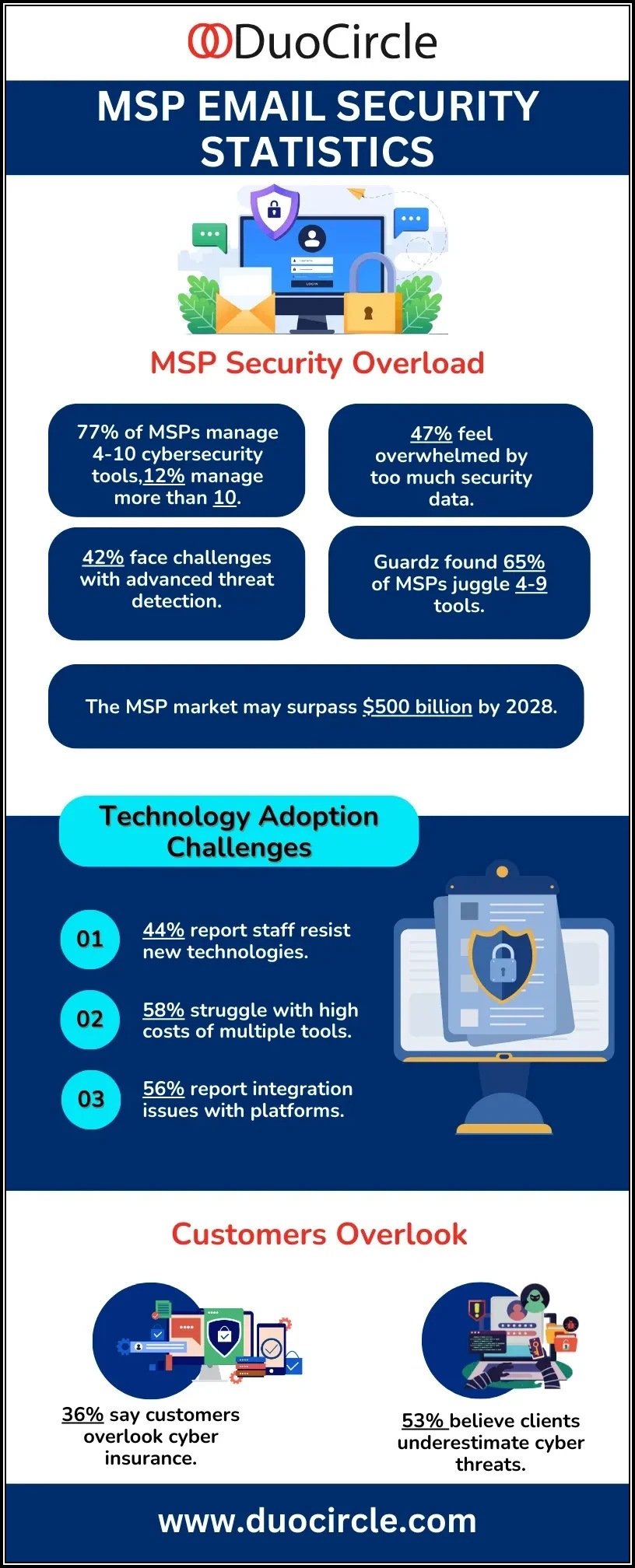
Managed services is a highly competitive industry that offers tremendous opportunities along with a unique set of challenges. Clients today expect managed service providers to provide increasingly seamless solutions using virtual interfaces. Quick, efficient responses to queries and technical support are also a must for retaining clients and ensuring satisfaction. Along with all this, MSPs must also contend with a scenario of rising cybercrime where a single incident can lead to catastrophic breaches and massive losses. To survive and thrive in such an environment, MSSPs need to leverage tools that will allow them to achieve all their stated goals while mitigating risks and meeting client expectations.
6 Essential Tools for Managed Service Providers
The following tools can enable MSPs to have a competitive edge needed to survive and thrive in the competitive and lucrative managed service industry.
Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR)
BDR tools safeguard against unwanted data loss by creating offsite backups to facilitate data restoration. Data loss is a serious issue faced by all organizations around the world. A recent study showed how the global average cost of data loss is $3.6 million. Despite the best precautions taken, factors like cyberattacks, human error, theft, power loss, or natural disasters can lead to data loss.
Such situations can cause reputational and revenue losses, lawsuits, and in many cases, even the closing down of an establishment. Fortunately, Backup and Disaster Recovery Tools, such as MSP backup solution from NAKIVO, are easy solutions to data loss, making them an essential tool for all different types of managed service providers.
Professional Services Automation (PSA)
Professional Services Automation tools are not directly linked to the services provided by Managed service providers. Instead, they assist MSPs in providing services to clients. Examples include billing tools, service desks, and project management tools.
A lack of automation can be a severe problem. Competition is fierce in managed services meaning that any MSSP that does not use automated tools is instantly at a disadvantage and loses out on revenue. Not using PSA tools also increases the time consumed by activities like handing client billing, service requests, and inventory management. If such activities are improperly handled, other adverse outcomes such as customer dissatisfaction can occur.
Such problems can be avoided by using professional service automation tools. PSA tools provide a competitive edge by enabling MSPs to efficiently handle business-related activities, save costs and deliver better services. This fact is further shown by a recent study which found that:
- PSAs reduce customer dissatisfaction by 48%
- Enhance response time by around 28%
- Improves the response time of Contracted service level agreements by 10%
Moreover, integrating these tools seamlessly into existing project management systems can significantly streamline task allocation and resource management, enhancing overall efficiency. Additionally, utilizing advanced analytics within project management tools can offer valuable insights into patch deployment strategies and optimization.
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM)
To live up to the managed services definition of being an organization that provides essential services in a bundled package, MSPs need to monitor and manage client IT infrastructure and systems remotely. Remote monitoring and management tools let MSPs deliver their services by enabling application and server monitoring, virtual machine management, and database administration.
One place where RMM tools shine best is their ability to detect and respond to incidents. The lack of rapid Incident response can have disastrous outcomes such as a dramatic rise in incident-related losses. Moreover, organizations without incident response plans are not compliant with PCI DSS Requirement 12.10. An untimely response to a breach can also lead to reputational losses with vendors, clients, and other stakeholders.
Since RMM tools streamline application monitoring, responding to incidents becomes much more manageable. While all RMMs allow monitoring, they differ in the number of management capabilities offered to the MSSPs. For example, while most provide some form of desktop controls, a few will also enable patch management and antivirus capabilities, further strengthening email security.
Remote Access Protocol
Remote access protocol tools include utility software that lets MSPs conduct remote management on a reduced and simpler scale than remote management and monitoring tools. An example of remote access protocol tool is Secure Shell (SSH) which lets MSPs access servers and desktops securely from remote locations. Often it can happen that MSPs do not need the capabilities of a full RMM suite. Situations can also arise where rapid troubleshooting is required, but it would be impractical to use an RMM. In all such cases, remote access protocols let MSPs quickly find solutions to any technical issues their client might be experiencing.
Patch Management Automation Tools
Patch management automation tools enable MSPs to deploy and manage patches in a centralized and automatic manner. They keep devices and systems up to date by applying patches as soon as they become available.
Not applying patches on time can compromise the integrity and efficiency of an IT system. Moreover, the chances of systems being compromised by human error increase tremendously if patches are not deployed in an automated manner. This lapse can lead to MSPs or their clients becoming victims of cyberattacks. Patch deployment is also very time-consuming when conducted manually, taking up valuable employee hours.
All this makes patch-managed automation tools vital regardless of the types of managed services provided by an MSP. Some other functions of patch detection tools include:
- Detecting and deploying driver updates
- Planning server or workstation tasks
- Carrying out automated processes
Malware Protection and Network Security
The final and most essential tool for any MSP is malware protection and network security services. These safeguard MSPs and their clients from various cyber threats like trojans, worms, ransomware, advanced persistent threats, cryptojacking tools, and more.
No Service provider can afford to compromise on cyber security. If an MSP gets breached, clients can lose mission-critical information and applications. That 60% of small organizations shut down just six months after an attack is an often repeated statistic but is still valid. Advanced persistent threats are also severe risks to organizations and can take hold if the proper focus is not placed on network security.
MSPs can leverage several tools such as security information and event management (SIEM), intrusion detection tools, enterprise virus defense, and log analysis tools to protect against cyber threats. Properly configured firewalls and virtual private networks also provide adequate protection against network intrusions and are a vital part of an MSPs toolkit.
Final Words
While the managed service industry faces several challenges such as cybercrime, increasing workloads, and ever-rising expectations, such problems are not insurmountable. MSPs can convert challenges to opportunities and thrive in the highly lucrative managed services sector by leveraging the correct tools and gaining a competitive edge.
If you are an MSP facing email-related issues at the client end, DuoCircle can help you tackle any issues and manage all your email problems in one place.