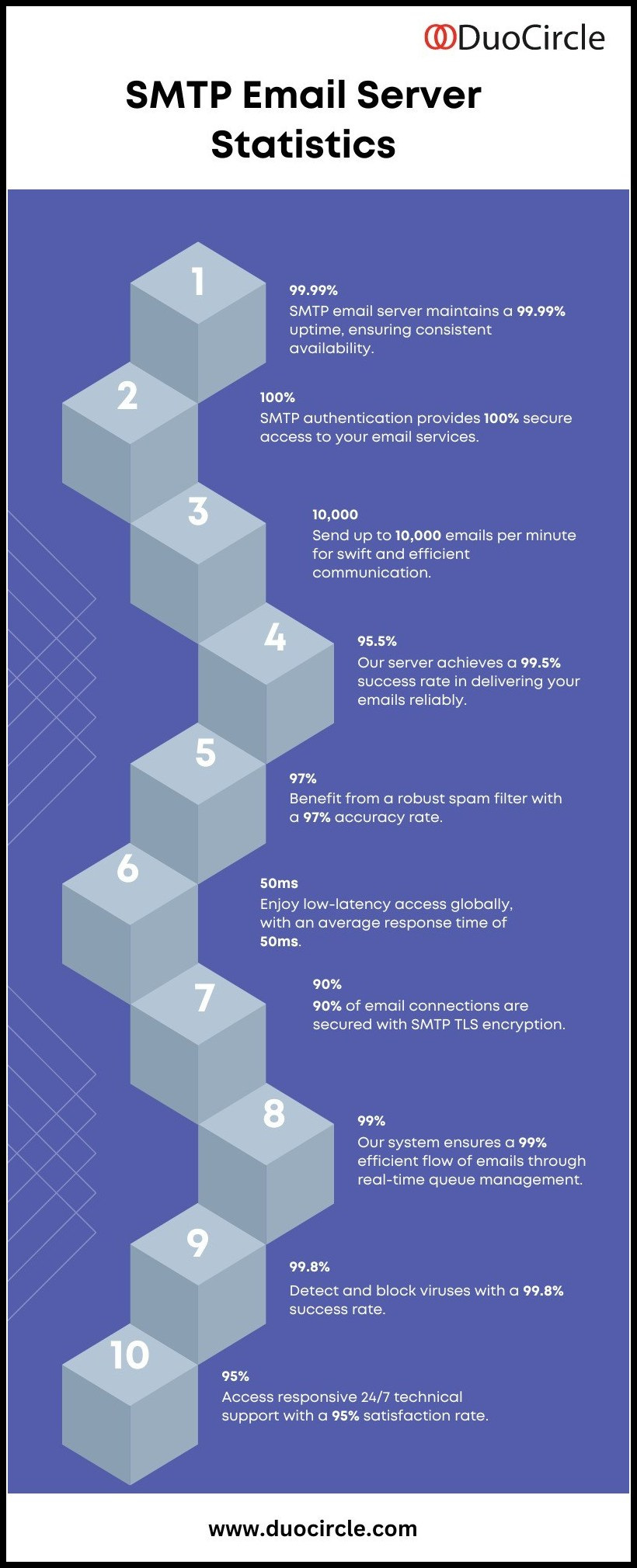
SMTP stands for ‘Simple Mail Transfer Protocol’, which is a generally accepted protocol used by all email systems to send messages over the internet. An SMTP Server facilitates this exchange of emails between two email systems by ensuring a hassle-free and quick transmission of a message from one server to another over TCP/IP networks. In other words, SMTP encompasses the processes taking place behind your computer screen while you send or receive an email.
What Is A Mail Server?
As the name suggests, a mail server is a system designed to send and receive emails. While many mail servers work along with the web servers in one particular machine, that isn’t the case for large ISPs and other public email domains, which often use their highly customized hardware servers for sending and receiving email.
Mail servers make use of their own set of email protocols to send and receive messages. For instance, an outbound SMTP server specializes in sending messages and handling outgoing mail requests, whereas IMAP and POP3 protocols deal more with receiving messages and processing incoming mail. To be precise, these protocols ensure that your messages reach the recipient once you log on to a mail server.
What Is SMTP Server?
It’s easy to understand SMTP keeping the traditional postal system in mind. We see that SMTP Server works like a post office that ensures that a letter from one person sitting in one region reaches another person sitting elsewhere without any tampering done to it. Just like a post office, an SMTP server is a computer running SMT Protocol that receives the messages sent to the server and then delivers it to the recipient, thereby ensuring zero loss of data. In other words, an SMTP server traces the journey of a mail leaving your inbox till it reaches the mailbox of the intended recipient.
What Is SMTP?
Having understood SMTP Server, let’s now look at SMTP or SMT Protocol. It is a protocol or set of commands that functions mainly to send, receive, and relay outgoing mail between email senders and receivers. It is mostly used to send messages from a mail client to a mail server, and that is why you must always specify the POP or IMAP server and the outbound SMTP server while configuring your email application. SMTP divides an email into coded parts while sending it to the recipient’s server. Upon reaching the recipient’s email server, the message undergoes decoding before it finally appears on the recipient’s mailbox.
SMTP Meaning For The Lay User
An SMTP server works in a chain wherein the address used by your mail client is used by the SMTP to decide which server to send the message to. The SMTP then relays the message to that particular server. A similar process works at the receiver’s end wherein his service provider downloads the message from the receiving server and places it in the recipient’s inbox.
The significance of the SMTP service can be fathomed by imagining its absence. In case SMTP is removed from the picture, there is no guarantee that a message won’t be lost in translation. When you send an email, it transforms into codes before it reaches the SMTP server. The SMTP server then processes the codes to revive the initial message. The simple elimination breaks this entire chain of SMTP.
Along with processing emails, SMTP also checks the authenticity of outgoing emails and protects you from fraudsters. In addition to this, SMTP automatically sends an email back to its sender if it’s undelivered, thereby notifying the sender about the incorrect or invalid email address.
How Does SMTP Work – The Technical Aspect
Since emails are so widely used for communication in today’s world (mainly for business communication), it is crucial to know how an SMTP server works behind the scenes.
- The SMTP server of the sender uses end-to-end message delivery to contact the recipient’s SMTP server on port 25.
- It then waits for the recipient’s server to send a 220 ‘Ready For Mail’ message.
- When the 220-message is received, the client-server sends a HELO command, which is then responded by the recipient’s server with a ‘250 Requested Mail Action Okay’ message.
- It is followed by the mail transaction, which starts with a MAIL command containing sender identification details.
- The sender then issues a series of RCPT commands that trace the email recipient(s). The recipient’s server responds with either a ‘250 Okay’ or a ‘550 No Such User Here’ message.
- Now the sender initiates a DATA command expressing its readiness to transfer a complete mail message. The recipient’s server responds with the message ‘354 Start Mail Command’.
- The sender now sends the message data followed by the string . indicating the end of message lines.
- The recipient server now acknowledges with a ‘250 Okay’ command.
- The server can now terminate the email delivery with a QUIT command to which the receiving server replies with a ‘221 Service Closing Transmission Channel’ response. Instead of QUIT, a new MAIL command may be generated to send another email. Or the TURN command may be used for a role reversal from sender to receiver.
How To Find SMTP Server?
There are multiple ways to find out what SMTP Server your system uses, such as running a set of commands on your DOS window or from the menu of MS Outlook or Control Panel. Here is the easiest way to find your SMTP Server through MS Outlook.
- Open Microsoft Outlook and click on ‘File’ on the left top corner.
- Click ‘Info’ on the left vertical bar.
- Open ‘Account Settings.’
- Your accounts are listed. Click on the account for which you want to check the SMTP info.
- You can now see complete information displayed regarding the incoming and outgoing SMTP servers for the selected account.
With the above information, you can now see what SMTP server your system uses, its features, and what kind of SMTP server suits your requirements. SMTP Server forms an integral part of email security and integrity. While most email service providers have SMTP incorporated, there is also a wide range of professional SMTP Server options that ensure a quicker and a higher rate of delivery of your emails.