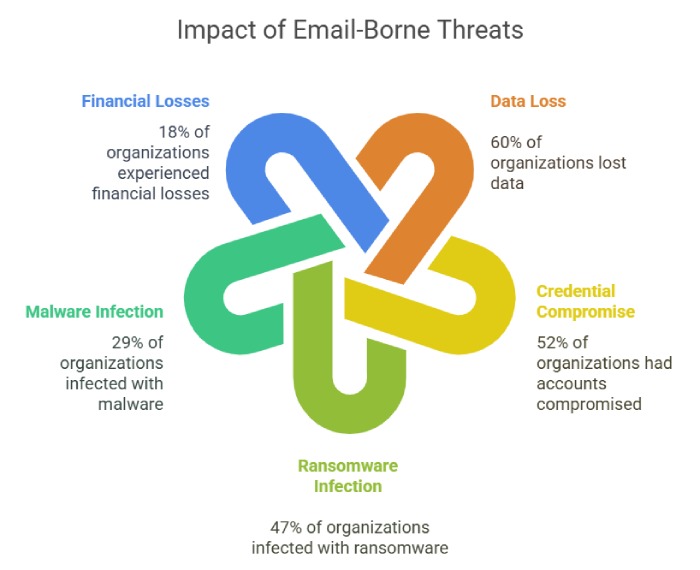
As they continue to grow in number, phishing emails have become a significant concern in the cybersecurity landscape. In October 2022, there were a staggering 101,104 unique email subjects associated with these fraudulent emails.
Phishing emails are typically designed to mimic official communications from reputable entities like banks, social media platforms, or government agencies. Within these deceptive emails, you might encounter links or attachments that, if interacted with, can lead to the installation of malware on your computer or device. Alternatively, they could redirect you to a counterfeit website, skillfully crafted to resemble the legitimate site of the organization being impersonated.
Red Flags of Phishing Emails
The Phishing Activity Trends Report, 4th Quarter 2022 highlights the ongoing concern of Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks in the corporate sector. What stands out is the substantial average target amount of $132,559, emphasizing the financial dangers posed by these attacks. Recognizing phishing attacks is crucial in safeguarding against such threats. Here are some red flags to look out for when it comes to identifying phishing emails:
Unusual Sender or Domain Name
Anything from rnicrosoft.com (which could pass for microsoft.com at a glance) to sender@microsoftcustomercare.com (instead of sender@microsoft.com) could be indicative of a fraudulent email.
Subject Line
Emails with subjects like “Immediate Action Required”, “User Account Suspended”, and so on should be read through with great care—even when they have the company’s logo on them—as these could be phishing attacks.
Urgent or Threatening Language
Phishing emails often employ language designed to create a sense of urgency or fear, pushing you to act quickly without considering the consequences. For instance, they may claim your account is on the verge of suspension or insist that you must immediately verify your personal information.
Requests for Sensitive Information
These emails often request sensitive details like your passwords, credit card numbers, or Social Security numbers. Legitimate companies will never make such requests via email.
Suspicious Links or Attachments
Phishing emails often include links or attachments that may be infected with malware. Clicking on a link or opening an attachment from a phishing email can potentially introduce viruses or other harmful software to your computer.
Poor Grammar and Spelling
Phishing emails often contain poor grammar and spelling errors. These errors often arise due to the content having been translated into English from another language. Legitimate companies will proofread their emails carefully before sending them out.
Unexpected Benefits
If you receive a message that promises a prize or benefit in return for a small fee or for free, it probably is a fake promise, and you should use caution.
Generic Greetings
Phishing emails often use generic greetings, such as “Dear Customer” or “Dear Valued Member.” If you receive an unexpected email that doesn’t address you by your name, it’s important to be cautious, as it may not be from a legitimate source.
While real companies may use email for communication, it’s important to note that genuine companies do not send emails containing links to update your payment information. Falling victim to phishing emails can have serious consequences, potentially leading to identity theft for individuals who unwittingly share their information with scammers. Plus, these fraudulent emails can tarnish the reputation of the companies they are impersonating.
What to Do If You Suspect a Phishing Email?
When you suspect that you’ve received a phishing email, it’s essential to take specific steps to protect yourself and your information:
Avoid Clicking on Links or Downloading Attachments
Resist the temptation to click on any links or download attachments within the suspicious email. These may lead to malicious websites or initiate malware downloads onto your device.
Verify the Sender’s Identity
If the email claims to be from a legitimate organization or business, independently verify its authenticity by reaching out directly through official contact information, such as a phone number from their official website. Do not use the contact details provided in the suspicious email.
Mark the Email as Spam or Phishing
To help protect others from falling victim to the same phishing attempt, mark the email as spam or phishing in your email client. This informs your email provider of the threat and may improve their spam filtering mechanisms.
Steps to take if You Accidentally Click on a Phishing Link
Even when we are on the lookout for any suspicious emails, accidents do happen. When you click on a link that prompts you to provide information or download a potentially harmful file, it’s crucial to follow these steps to minimize potential damage:
Stay Calm and Act Quickly
The first step is to stay composed. Panic can cloud judgment. By maintaining a clear mind, you can proceed more effectively in resolving the issue.
Do NOT Interact With the Website
Be wary of clicking on any links, providing any information, or accepting cookies. If you find an automatic download initiated, cancel the process immediately.
Change your Passwords
Immediately change the passwords for any accounts that may have been compromised. This includes email, banking, and social media accounts. Use strong, unique passwords for each account to enhance security.
Check your Financial Accounts
Thoroughly review your financial statements and accounts for any unauthorized or suspicious transactions. Contact your bank or credit card company to report any discrepancies and seek their guidance.
Report the Incident to the Appropriate Authorities
Contact local law enforcement, your country’s cybersecurity agency, or any relevant reporting channels to inform them about the phishing incident. They can provide guidance and potentially take legal action against the perpetrators.
Monitor for Identity Theft or Fraud
Continue to monitor your accounts and credit reports for any signs of identity theft or fraudulent activity. Consider signing up for identity theft protection services to receive alerts about any unusual activity related to your personal information.
Being swift and thorough in your response to a phishing attack can minimize the potential damage and help protect your online identity and financial well-being.
Preventive Measures
Implement email filtering and security software
These tools automatically detect and block phishing emails, safeguarding your inbox from potential threats.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication
2FA adds an extra layer of security to your accounts, making it significantly harder for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access.
Educate Employees or Family Members About Phishing Risks
Raising phishing awareness training and providing education helps users recognize and avoid phishing attempts, reducing the likelihood of falling for scams.
Regularly Update and Patch Your Software and Operating Systems
Keeping your software up to date strengthens security, closing known vulnerabilities and making it more challenging for attackers to exploit weaknesses in your system.
Phishing attacks are a serious threat to individuals and organizations alike. By being aware of the red flags of phishing emails and by implementing effective phishing protection measures, you can help avoid falling victim to these scams.