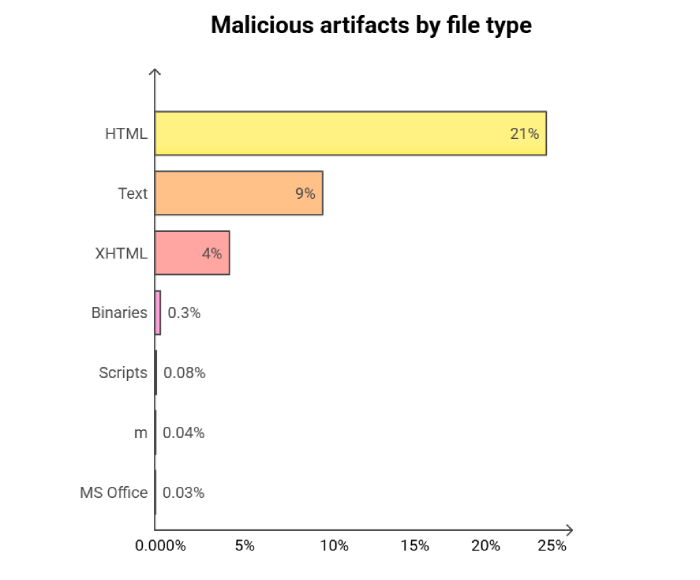
Researchers are suggesting that the use of malicious HTML files by attackers remains quite potent. Although around for a while, attackers still prefer this method because of its effectiveness. Follow this article to know more about why malicious attachments remain the attackers’ favorite and tips to safeguard yourself.
According to a recent study, security researchers have cautioned that cybercriminals increasingly use malicious HTML files to carry out attacks. The study by Barracuda Networks also reveals that malicious files now make up half of all HTML attachments sent through email, which is twice as much as last year’s figures.
Interestingly, this increased prevalence of malicious HTML files doesn’t seem to result from mass attack campaigns where hackers send the same attachments to many people.
As a result, it is crucial to have appropriate cybersecurity measures in place now more than ever. According to the report, it is how organizations can prevent falling victim to such attacks.
What are Malicious Attachments?
Malicious email attachments are designed to launch an attack on a user’s computer. The attachments within these malicious emails can be disguised as documents, PDFs, e-files, and voicemails. Attackers attach these files to emails that can install malware capable of stealing information and destroying data.
Some of these infections can allow hackers to take control of the user’s system, giving them access to the screen, capturing keystrokes, and accessing other network systems.
Why are HTML Attachments Hackers’ Favorite?
HTML is a commonly used language for displaying web content and has legitimate uses in email communications. For instance, an enterprise employee may receive reports generated by applications and tools sent via email in HTML format. Since this is a common practice, users usually don’t suspect anything when encountering such attachments, and email security gateway filters cannot entirely ban them.
Nonetheless, it is vital to remain vigilant as attackers often use malicious HTML files to spread malware through email attachments. Thus, having proper security measures in place to scan and detect such files is crucial.
In the report, the researchers mention that hackers use HTML attachments, including JavaScript code, that redirect victims to a phishing site. Imagine you receive an email that looks like an automated notification of a DHL parcel, and when you open the HTML attachment, you see a copy of the DHL login page.
In other cases that researchers noted, the HTML attachments included links that lured users to download a file that’s actually a malware payload.
“Furthermore, in some cases we observed, the HTML file included sophisticated malware with an embedded malicious payload, including potent scripts and executables,” the report mentions. “It is an attack technique that hackers use more than those involving externally hosted JavaScript files.”
Steps to Stay Safe
Since malicious files can cause damage to your device and organization, it’s essential to take the necessary steps to protect yourself from them. Here’s how to stay safe against such attempts:
- Set Up a Secure Environment: Your email infrastructure will be crucial here. Make sure you regularly update the antivirus software and firewall. Furthermore, a solid Data Loss Prevention strategy is vital. The best way to secure your communications is by defining DMARC protocols for your domain.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication: You must use two-factor authentication coupled with zero-trust access solutions. They will evaluate the credentials, the user’s device, location, time zone, and history and limit breaches even if your employees fall victim to credential theft and phishing.
- Avoid Opening Emails from Untrusted Sources: Many users fall for phishing attempts because they don’t know which email attachments can contain something malicious. Most of them open any email they get without checking their source. Your team must avoid opening emails from unknown sources. It applies to all emails coming from an inside or outside source.
- Practice Good Password Hygiene: We saw that keystroke loggers and password collectors are the most common malicious attachment types that hackers use. You can prevent such attacks by maintaining good password hygiene. Hence, make sure you change your passwords frequently. The recommended password lifespan is three months.
If it seems too bothersome, then focus on creating a strong password using a combination of special characters, sentences, different cases, and numbers.
- Employee Training: It’s essential to provide employees with training on how to recognize and report any malicious HTML attachments they may encounter, especially those coming from unknown sources. It is crucial to prevent cybersecurity threats from harming the organization.
Additionally, businesses must have incident response tools and procedures that can efficiently remove malicious attachments from all mailboxes that receive them. Doing so can protect the entire organization from potential cybersecurity risks.
Final Words
No network is 100% safe against malicious attachments. That is why it is vital to know everything you can about them. Cybercriminals always think of new ways to scam victims, but emails containing malicious HTML attachments aren’t going anywhere.
We discussed ways you can protect your customers and business from such threats. Setting up a secure environment and knowing which email attachments can contain something malicious is an excellent start.