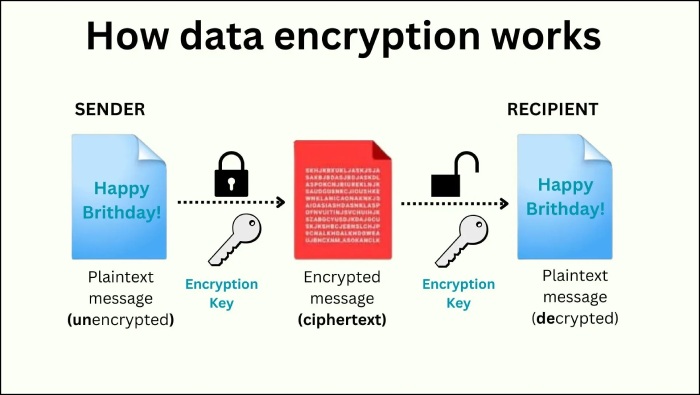
Modern email encryption protocols have revolutionized email security. Let us learn about the latest email encryption protocols that protect sensitive data, prevent eavesdropping, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Emails have become one of the most common forms of exchanging information. Hence, it has become essential. But is it safe to exchange sensitive information through emails? Are there risks associated with it because threat actors keep looking for innovative ways to access email servers, intercept confidential information, and exploit it to satisfy their nefarious intentions?
The primary email encryption techniques are no longer secure because cyber threat actors have advanced their technologies significantly. Therefore, securing your emails requires implementing the latest email security protocols. This article discusses modern email encryption protocols and explains how they enhance email security.
Modern Email Encryption Protocols – An Overview
With cybercriminals using innovative ways to attack email servers, securing the confidentiality of sensitive information gains more significance. Therefore, modern email encryption protocols are necessary to achieve this objective.
1. S/MIME [Secure – Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions]
S/MIME is an effective email encryption protocol and a convenient and accessible solution for securing email communication. It provides a secure means of sending/receiving widely used email messages by integrating into various email clients and webmail platforms.
S/MIME uses PKI, a critical public infrastructure for encrypting and decrypting email messages. Thus, it protects the messages against interception and enhances their confidentiality. The infrastructure uses a root certificate authority (CA), an IT administrator, to distribute digital certificates to employees. It binds their identity with the Public Key.
Since these certificates are delivered through the corporate email system, employees can share encrypted messages securely and comfortably.
2. Open PGP [Open Pretty Good Privacy]
PGP, a renowned software program, enables users to encrypt email messages, authenticate them with digital signatures and encrypt stored files. PGP was developed initially in the early 90s and widely adopted as the best standard for securing email communication, especially among organizations and individuals with high data privacy and security demands.
However, PGP today refers to any encryption program following the OpenPGP public key cryptography standard. Thus, it provides a standardized approach to secure email messaging.
PGP uses symmetric-key and public-key encryption for securing email messages and attachments. As a result, it becomes challenging for unauthorized users to access the content. Though PGP is no longer considered a dominant email encryption program, it is popular among individuals and organizations prioritizing data privacy and security.
3. GPG [GNU Privacy Guard]
GPG is a free, open-source encryption software that provides end-to-end encryption to secure emails, files, directories, and disk partitions. It is an advanced version of OpenPGP because it combines asymmetric and symmetric cryptography.
GPG protects data by converting plain text into a complex code of unreadable characters, ensuring user communication privacy and making it difficult for unauthorized users to access the content.
Furthermore, GPG allows users to sign files with embedded digital signatures. Therefore, it addresses data authentication and non-repudiation issues. Besides, it authenticates the sender’s credentials to prevent them from denying their active involvement in the communication.
4. TLS – Transport Layer Security
TLS provides data security and privacy for internet communication. Generally, it is used for encrypting web applications and server communications, like internet browsing. However, it can also be applied for encrypting emails and messages. TLS requires the installation of a TLS certificate, popularly known as an SSL certificate, on the original server of the website or the application.
A certificate authority to the domain owner issues the SSL certificate. It contains essential information about the domain ownership and the server’s public key required for validating the server’s identity. The TLS handshake occurs between the web server and the client’s device when the user accesses the website by initiating a TLS connection.
5. SMTPS – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Secure
While SMTP provides secure transmission of email messages over the internet, SMTPS extends the security by encrypting email communication using SSL or TLS encryption protocols.
When an email client sends an email over SMTPS, it connects to the server and initiates the SMTPS protocol for authentication. Once mutually authenticated, the server and the client negotiate the encryption level used for email transmission.
Since SMTPS encrypts emails, it protects against tampering during transit and eavesdropping. Therefore, it is a secure way to send an email online. However, SMTPS has become less popular than STARTTLS because the latter provides the same level of security while maintaining compatibility with legacy email systems.
6. STARTTLS – Transport Layer Security
We have seen that SSL and TLS protocols encrypt communication channels between computers over the internet. STARTTLS, an email protocol command, allows the client to upgrade an existing insecure connection to a secure one using TLS or SSL. It is generally used with SMTP and IMAP. However, POP3 uses the SLTS command.
STARTTLS does not require additional ports or protocols to enable secure communication between clients and email servers.
When a client uses STARTTLS to connect to an email server, it sends a message requesting a secure connection. Therefore, if the server supports STARTTLS, the client and email server negotiate the encryption protocol to use and exchange the cryptographic keys to encrypt and decrypt messages. While STARTTLS protects the data in transit, it does not secure the data at rest.
7. SMTP MTA-STS – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol – Mail Transfer Agent – Strict Transport Security
SMTP MTA-STS is a robust email security mechanism that uses SMTP to enforce TLS when communicating between email servers. MTA-STS enables a domain to declare in its DNS that it supports TLS encryption for email delivery. Therefore, when an email server tries to deliver an email to an MTA-STS-enabled domain, it checks the DNS records for MTA-STS policies.
On finding the policies, the sending email server establishes a secure TLS connection with the receiving server to send the email. MTA-STS ensures email delivery over a secure and encrypted channel. Thus, it protects against Man-in-the-Middle and eavesdropping attacks.
8. Digital Certificates
A Digital Certificate is a robust encryption tool that secures email communication cryptographically. They constitute a specific type of public key encryption by utilizing a pair of cryptographic keys to encrypt and decrypt messages.
Digital certificates allow users to send encrypted emails using a predetermined public encryption key for encrypting outgoing mail. Thus, it acts as a virtual passport linked to your online identity. So, it is primarily used to verify and validate that identity.
Individuals, business entities, government organizations, email servers, and other digital entities can use Digital Certificates to validate their online identity and ensure the security of their communication.
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are used in conjunction with encryption protocols to provide comprehensive email security. However, they do not technically qualify as encryption protocols. Instead, they are authentication protocols.
Final Words
Email security has evolved considerably, with modern email encryption protocols offering robust tools for protecting sensitive information. Individuals, business entities, and organizations can reduce the risks associated with email communication and enhance their security posture by understanding and implementing the email encryption protocols discussed here.
However, with evolving technology, staying updated with the latest email protocols is essential to protect sensitive information.